Decision support to select appropriate Sustainable Land Management (SLM) practices within the landscape
-
Conservation Tillage Practices for Corn Production
"Tipid Saka"
A crop production system which focuses on soil conservation and reducing excessive tillage operations, reduces labor and farm inputs while increasing productivity and profitability.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform plains
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure untitledland (leased)
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Chemical Soil Deterioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic measures: Prevention and mitigation/reductionTechnical function increased soil fertility and good soil structure for better nutrient and water uptake by plants
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment input and cost per ha: Labor - 6,950 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seeds, fertilizer, biocides, Bio-N) - 4,400 P/ha; Others (post harvest, market transport and packaging) - 10,810 P/ha. Total Cost - 22,160 P/ha.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.83 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.67 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.84 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.52 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.86 Medium
-
Natural Vegetative Strips (NVS)
Within individual cropland plots, strips of land are marked out on the contour and left unploughed in order to form permanent, cross-slope barriers of naturally established grasses and herbs.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500 -1500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-3000
Landform footslopes; hillslopes
Slope rolling-hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-80; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-20
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, trees and shrubs: rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of top soil; surface erosion; gully erosion; chemical soil deterioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter.
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Vegetative Measures; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Reduction of slope angle; reduction of slope length; control of dispersed runoff; increase infiltration and increase soil fertility
Establishment input and cost per ha Establisment activities: Lay out of contour using A-frame; placing wooden pegs along contours; seeding; transplanting; land preparation. Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 1000 P/ha; Equiipment (animal traction, tools, and stakes) - 3,300 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seeds, seedlings, fertilizer, biocides) - 9,000 P/ha; Total Cost - 13,300 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Plowing along the contour leaving unplowed strips; planting; mulching; fertilization, interim cultivation/weeding; plowing mulch into the soil; weeding slashing grass; spreading the cut materials evenly in the alleys; pruning. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and cost per ha per year: Labor -1,700 P/ha-year; Equipment (animal traction, tools) - 1,980 P/ha-year; Agricultural inputs (seeds, fertilizer, biocides) - 7,500 P/ha-year; Total maintenance cost - 11,180 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.81 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.56 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.95 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.63 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.95 Medium
-
In 'situ' Decomposition of Banana Stalk
"Palata System"
Leaving the trunk of a newly harvested banana standing beside a follower plant to provide nutrients and moisture especially during period of drought.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) < 100
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform plateau/plains
Slope flat-gently sloping
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level >120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 2-5; 500-1,000
Land tenure company leased
Landuse Perennial (non-woody) cropping, full irrigation
Land degradation Chemical soil detrioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, water degradation; aridification
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic Measures: Mitigation/reduction and rehabilitationTechnical function Increase soil fertility; Increase/maintain water stored in the soil
Establishment input and cost per ha Maintenance/recurrent activities: 1) Cutting of crown of newly harvested plants; Inputs: Labor - 2,350 P/ha-year; Equipment - cutting tools - 500 P/ha-year; Total Cost - 2,850P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.63 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.02 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.65 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
2.99 Negligible
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.29 Low
-
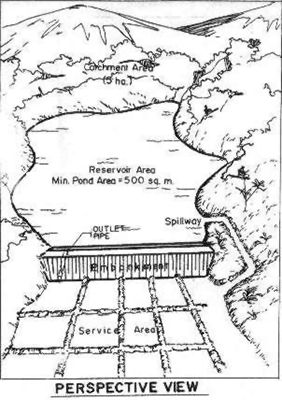
Small Water Impounding Project (SWIP)
Development of micro-catchment for soil and water conservation and for the provision of supplementary irrigation during the dry season.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-3000
Landform hillslopes; valley
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 80-120 ; >120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping; perennial crop
Land degradation Water degradation, aridification
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures; Mitigation/reduction and rehabilitationTechnical function Water harvesting nd increase water supply
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Clearing, staking and laying out; Stripping and excavation; embankment filling; pipe lay out and installation; riprapping; concrete works, embankment sodding; and canal excavation and lining. Establishment inputs and cost per ha of service area: Labor - 105,000 P/ha; Materials - 99,000 P/ha; 96,000 P/ha; Total Cost - 300,000 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent costs (Embankment maintenance, appurtenant structures maintenance, canal maintenance): Labor - 12,000 P/ha-year; Minor equipment - 3,000 P/ha-year; Total maintenance cost - 15,000 P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.26 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.62 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.05 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
4.04 High
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.97 High
-
Small Farm Reservoir (SFR)
"Tabon"
The Small Farm Rerservoir is an earth dam structure used to trap harvest and store rainfall and water runoff.
Location lowland; upland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) < 100; 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform plains/hillslopes
Slope rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; low organic matter content
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping
Land degradation soil erosion and excessive runoff; limited water supply
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures: Prevention and rhabilitationTechnical function Water harvesting/ increase water supply; Control dispersed runoff, retain/trapped; contol concentrated runoff: retain/trap.
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: 1) Laying-out & staking; 2) Clearing; 3) Excavation; 4) Spreading of fill materials; 5) Embankment filling and compaction; 6) pipe laying out and setting; and 7) canal/spillway construction. Total construction cost - 40,000 - 100,000 P/unit.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.03 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.40 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.96 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.97 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.36 Medium
-
Multi-Storey Cropping
"Maramihang Pagtatanim or Planting in Great Numbers"
Cultivating a mixture of crops with different heights (multi-storey) and growth characteristics which together optimise the use of soil, moisture and space.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform footslopes, ridges, and plateau/plain
Slope gentle - moderate
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 80-120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Agroforestry, rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of top soil/surface runoff; chemical soil deterioration; fertilit decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Vegetative Measures; PreventionTechnical function Control raindrop splash; improvement of ground cover
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment actvities: Planting of tallest storey (coconut); Planting of lowest storey (pineapple); Planting of lowest storey continued (root crops); Planting of middle storey (coffe and banana). Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 7,000 P/ha; Equipment (animal traction and farm tools) - 4, 230 P/ha; Agricultural (seedlings, fertilizer, biocides, compost/manure) - 54,000 P/ha; Total Cost - 65,230 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha per year: Labor - 14,100 P/ha-year; Agricultural (fertilizer, biocides) - 9,000 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.40 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.97 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.21 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.98 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 16.56 High
-
Residue Incorporation (Corn)
"Palugdang", "Palata"
Incorporation of corn stalks during land preparation for the succeeding crop.
Location upland to hillyland and highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-1500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-3000
Landform footslopes- hillslopes; plateau/plains
Slope gentle-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50 - > 120 ; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-5
Land tenure titled, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline; and reduced organic matter content
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic Measures: RehabilitationTechnical function Increase soil fertility and organic matter
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Equiipment (animal traction) - 1,500 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seeds, fertilizer, biocides) - 7,700 P/ha; Others (planting, Harvesting, Maintenance) - 4,500 P/ha; Total cost - 13,700 P/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.56 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.04 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.98 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.16 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.74 Low
-
Planted Vegetative Strips (PVS)
Planting of economic crops/forages in strips along the contour to control soil loss through erosion.
Location lowland; upland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100; 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-2000
Landform hillslopes; plateaus/plains
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of top soil; surface erosion
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic Measures; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Control; dispersed runoff; imped and retard
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Planting of Alley crops; contouring; planting of vegetative strips. Establishment inputs and costs: Labor - 950 P/ha; Equipment (animal traction) - 600 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seeds and seedlings) - 5,300 P/ha. Total Cost - 6,850 P/ha.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.81 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.69 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.94 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.53 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.97 Medium
-
Windbreaks
Planting of herbaceous plants or trees along property boundaries to serve as windbreaks and as sources of fodder and fuel.
Location lowland; upland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) < 100; 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform footslopes; hillslopes
Slope rolling-hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level > 120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse agro-silvo pastoralism, rainfed
Land degradation soil erosion by wind, loss of top soil
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; PreventionTechnical function Reduction in wind speed
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment inputs and cost per ha (seeding /planting): Labor - 1,880 P/ha'; Tools - 250 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seedling, stem cuttings) - 800 P/ha. Total Cost - 2,930 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Removal of dead branches (trees); Cutting of grasses. Maintenance/recurrent cost per ha per year: Labor - 700 P/ha-year; Minor tools - 300 P/ha; Total recurrent cost - 1,000 P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.57 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.44 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.66 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.32 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.99 Low
-
Rainfed paddy rice terraces
"Palayan"
Terraces supporting rainfed paddy rice on steep mountain slopes: these have been in existence for more than a thousand years.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 1500-2500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-3000
Landform mountain slopes
Slope hilly - steep
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 80-120; > 120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha)
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of topsoil/surface erosion; chemical soil deterioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures (Bench Terraces); Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Control of dispersed runoff: retain trap; increase/maintain water stored in the soil; reduction of slope angle; reduction of slope length; indirect maintenance of fertility
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Levelling by moving soil from upslope to the downslope part; construction of bunds (lip at the terrace ridge) of about 50-100 cm; determination of contour lines. Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 115,000 P/ha; Equipment - 10,000 P/ha; Total cost - 125,000 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Weeding by cutting grasses on the bund/riser using hand tools, hoeing; Land preparation by puddling, in most cases the use of animal traction is not possible because of the steepness of the slope and height of the risers; Repairing breached portion of the bunds, adding few centimeters in the process. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha per year: Labor - 3,000 P/ha-year; Equipment (farm tools) - 1000 P/ha-year; Total maintenance cost - 4,000 P/ha-year. Remarks: The costs of establishment are just estimates as new terrace construction no longer takes place in the study area. The land has already been terraced for centuries. The maintenance costs assumes minor and light maintenance and does not include major repairs of bunds.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.91 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.67 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.93 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.69 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.20 Medium
-
Stone bunds and small basins
"Pamugong sa yuta (Cebuano)"
Piling of stones and rocks along the contour to control run-off and soil erosion. It is also about the creation of small basins by removing stones and using them as barriers.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1,500-2,000
Landform hill slopes
Slope rolling - hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level > 120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Surface soil erosion, top soil removal
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures; Mitigation and rehabilitationTechnical function control of concentrated runoff; retain/trap
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Contouring; gathering and piling of stones along contour with development of small basin for rainwater impoundment. Establishment inputs and cost per ha. Labor - 47,000 P/ha; Equipment - 1,000 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 1,800 P/ha.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.46 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.15 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.50 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.47 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.58 Low
-
Vetiver grass system or Vetiver grass technology
"Mora, Moras, Amora and Modas in the different regions in the Philippines"
Vetiver grass used as contour hedgerows in sloping agricultural land used for annual crops.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform hillslopes
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80 ; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping rainfed
Land degradation Surface erosion by water, loss of top soil
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; Mtigation and preventionTechnical function control dispersed runoff, retain top soil; reduction of slope length
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Planting vertiver grass along contour; Replacement/replanting gaps. Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 2,350 P/ha; Seedlings - 4,700 P/ha; Total Cost - 7,050 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Pruning. Maintenance and recurrent inputs and cost per ha per year: Labor - 1,000 P/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.38 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.14 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.77 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.51 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.80 Low
-
Littuko Growing for Forest Enhancement
Growing of rattan is done by upland farmers as part of the Community Based Forest Management (CBFM).
Location upland to hillyland and higland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500; 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform hillslopes
Slope hilly to steep
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50-1
Land tenure communal, organized
Landuse Natural;; Other: Grazing land; forest
Land degradation Biological degradation: reduction of vegetation cover; loss of habitat
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; RehabilitationTechnical function Promotion of vegetation species and varieties; conservation of trees that serve as hosts; increase organic matter; increase biomass
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Nursery establishment through seedbed; transplanting. Establishment per unit: Labor - 400 P/unit; Agricultural inputs (incl. seeds) - 10,400 P/ha; Total Cost -10,800/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.65 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.48 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.93 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.39 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.45 Medium
-
Rockwall Terracing
Rockwall terracing refers to the piling of stones or rocks along contour lines to reduce soil erosion in hilly areas.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform hillslopes-mountain slopes
Slope rolling - hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure not titled, individual
Landuse Annual cropping; mixed grazing land, rainfed and irrigated
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of topsoil/surface runoff
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Strucutural Measures; RehabilitationTechnical function control of dispersed runoff: retain trap; retain /trap; control concentrated runoff: retain trap; control soil erosion
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Contouring; Digging along contour; Gathering and piling of stones along contour. Establishment inpputs and costs per unit (ha): Labor - 37,800 P/ha; Equipment - 1,000 P/ha; Total cost - 38,800 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent of activities: Re-piling of stones and rocks that are dislodged. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per unit (ha) per year: Labor - 1,000 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.30 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.19 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.66 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.28 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.43 Low
-
Seed Production of Multipurpose Shrubs/Legumes
Seed production of multipurpose shrubs and legumes, a soil conservation practice in sloping areas wherein flemingia (Flemingia macrophylla) and Indigofera (Indigofera tinctoria) are densely planted along contours.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform hillslopes-mountainslopes
Slope rolling-hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50-1
Land tenure titled, individual
Landuse Trees and shrubs cropping: Forests/woodlands: natural cropland
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of topsoil/ surface runoff; chemical deterioraton-fertlity decline; biological degradation
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; RehabilitationTechnical function control of dispersed runoff-retain/trap; control of concentrated runoff; retain/trap; improvement of ground cover; promotion of vegetation species and varieties
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Land preparation; Plowing, harrowing and furrowing; Establishment of contour lines and laying out. Establishment inputs and costs per unit (ha): Labor - 2,300 P/ha; Equipment (bamboo pegs) - 150 P/ha; Seeds - 2,100 P/ha; Total Cost - 4,550 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Weeding/hilling-up; Harvesting; Sun drying; Manual threshing; Harvesting of Flemengia and Indigofera. Maintenance/recurrent costs: Labor - 2,100 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.06 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.47 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.95 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.41 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.89 Medium
-
Contour Farming Using Hedgerows
"Contour Farming"
Contour farming is a technology practiced in sloping areas in which hedgerows are established along the contours and other annual/cash crops are grown in the alleys between the hedges.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform hillslopes-mountain slopes
Slope rolling - hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) < 0.50
Land tenure not titled, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of topsoil/ surface erosion; chemical deterioration; fertillity decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Vegetative Measures; RehabilitationTechnical function Conrol of dispersed runoff: retain/trap; minimize soil erosion due to runoff; serve as soil nutrient traps
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Laying out and establishment of contour lines/hedges; Planting of hedgerows with Napier grass; Planting of perennial crops along contour. Establishment inputs and costs per unit (ha): Labor - 1,350 P/ha; Local materials (A-frame) - 100 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seedlings, herbecides) - 4,400 P/ha; Total cost - 5,850 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Land preparation of alley between hedges; furrowing; planting of corn (first cropping); Weeding; Harvesting of first crop; Planting of second crop (corn & peanut; Weeding; Harvesting of second crop. Maitenance/recurrent inputs and cost per ha per year: Labor - 1,950 P/ha-year; Equipment (animal traction)/ - 300 P/ha-year; Agricultural inputs (seeds and fertilizer) - 2,200 P/ha-year: Total maintenance cost - 4,450 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.03 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.76 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.08 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.90 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.77 High
-
Vegetable Terracing
Vegetable terracing is a technology practiced at which point terraces are established from the contours along mountain slope for crop production.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 2000-2500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform hillslopes-mountainslopes
Slope rolling-hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50;low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50-1
Land tenure titled, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, Forest/woodlandrest/woodlands
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of topsoil/surface erosion; chemical soil deterioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Structural Measures; Mitigation/ReductionTechnical function Control of dspersed runoff: impede/retart; control concentrated runoff: impede/retard; reduction of slope angle
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Establishment of terraces. Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 25,100 P/ha; Minor tools - 600 P/ha; Total cost - 25,700 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Land preparation; application of chicken manure; Planting; hilling up including application of fertilizer; Weeding; Spraying of insecticides; Harvesting. Maintenance/recurrent costs per ha per year: Labor - 14,570 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (fertilizer, compost/manure, insecticides) - 43,300 P/ha-year. Total maintenance/recurrent costs - 57,870 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.16 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.88 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.82 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.56 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.42 Medium
-
Alternate Wetting and Drying
Alternate Wetting and Drying is a water-use management technique wherein irrigation water input could be substantially reduced to as much as 35% without significantly affecting rice yields.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) < 100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform plain
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level > 120 ; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50-1
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual Cropping, irrigated
Land degradation Water degradation, change in quantity of surface water
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Management Measures- Major changes in timing of activities; PreventionTechnical function More efficient water use
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: 1) Preparation of PVC/bamboo tubes; 2) Perforating the sides of the tubes with many holes; Establishment inputs and cost per unit: Labor - 160 P/pc; Materials: PVC - 210 P/pc; Total Cost - 370P/pc
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.88 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.33 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.92 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.59 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.72 Medium
-
Trees as Buffer Zones
Trees as buffer zones are vegetative measures established in the area to prevent pest from crossing in between blocks. Further, the technology provides haven for flora and fauna which are endemic in the area.
Location upland to hillyland; highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500; 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform hillslopes; valley
Slope gentle - moderate
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; 80-120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Trees and shrubs
Land degradation Biological degradation; loss of habitats
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; Mitigation and preventionTechnical function Control of raindrop splash; control of dispersed runoff; stabilization of soil; reduction in wind speed; increase biomass; spatial arrangement and diversification of land use; improve biodiversity
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Grass Brushing; Hole Digging; Planting. Establishment inputs: Labor - 5,500 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent cost per hac per year: Labor - 3,700 P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.80 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.63 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.08 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.66 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.17 Medium
-
Pressing of Cogon Grass (Imperata cylindrica)
An indigenous technology of enhancing wildling growth by pressing of cogon grass.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform hillslopes; mountain slopes
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 50-100
Land tenure Lands owned by the state; Land user rights: open access (unorganized)
Landuse Natural; Deforested Land
Land degradation Biological degradation; loss of habitats
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures, Others (Suppressing of Cogon; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Enhance the growth of wildling by controlling the growth of fast-growing grasses (cogon); control/avoid forest fires
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Identification of wildlings (2 feet high); Ring weeding; Pressing of cogon away from wildlings; Application of fertilizers. Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 950 P/ha; Construction material (wood and rope) - 200 P/ha; Total Cost - P 1,150 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Pressing of Cogon (Labor) - 210 P/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 2.68 Negligible
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
2.52 Negligible
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.22 Low
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
2.67 Negligible
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 11.09 Low
-
Firebreaks/Greenbreaks
Gaps in vegetation or other combustible material that act as barriers to prevent and/ or control the spreading of forest fires to other areas.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform hillslopes; mountain slopes
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 50-100
Land tenure Lands owned by the state; Land user rights: open access (unorganized)
Landuse Plantation; afforestation, tree generation
Land degradation Biological degradation; detrimental effects of fire
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures, Others (Suppressing of Cogon; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Control fires; reduction of dry materials (fuel for wildfires)
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Clearing of Cogon in the firelines; Planting of kakawate cuttings. Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 1,250 P/ha. Maintenance: 500 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.11 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.16 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.86 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.36 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.49 Low
-
Ecological engineering for irrigated lowland rice ecosystem
Ecological engineering for lowland rice ecosystem by promoting and planting of flower strips in rice fields.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform plateau/plains
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 0-20; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5-1
Land tenure titled land, individual; water use rights- communal (organised)
Landuse Annual cropping, full irrigation
Land degradation Biological degradation: increase of pests/diseases, lost of predators
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; Others (Annual Flower Strips; Prevention and Mitigation/ReductionTechnical function Biological control reduces pollution by agro-chemicals
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Flowering plant seed collection; flowering plant nursery establishment; transplanting flowering plants. Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 4,730P/ha; Agricultural inputs (fertilizer, compost/manure - 1,600 P/ha; Total Cost - 6,330 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Flowering plant maintenance, i.e. trimming, removal of volunteer seedlings out of the strips and thinning during cropping season; Watering and replacement in times of long drought fallow period. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha per year: Labor - 1,880 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.08 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.87 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.05 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.64 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.64 High
-
Sediment Traps
"Catch basin, silt traps, cascading canals, trenches, ditches"
Sediment traps are structures built in the area which includes cascading catchment canal, silt traps and catch basin along perimeter, between pineapple fields and along diversion ditches to collect run-off during rains, preventing and minimizing the eroded soils cascading into natural bodies of water.
Location upland to hillyland; highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500; 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform hillslopes; valley floors
Slope gentle - moderate
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; 80-120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual; land user right - leased
Landuse Perennial; non-woody: Other: waterways, drainage lines, ponds, dams (after)
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of top soil; surface erosion
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures (Cascading canals and Silt Traps); Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Sediment retention/trapping, sediment harvesting; Control of dispersed runoff; retain/trap, impede/retard; control of concentrated runoff; retain/trap, impede/retard, drain/divert.
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activiteis: Excavation of canal; construction of bed; constructiobn of trenches. Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 2,530 P/ha; Equipment - 3,360 P/ha. Maintenance activities: Desilting. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha: Labor - P7,300 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.33 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.12 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.79 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.60 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.84 Low
-
Contour Straight Block Layout
It is a package of soil and water conservation technology that integrates contouring, bedding, and blocking.
Location upland to hillyland; highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500; 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform hillslopes; valley
Slope gentle - moderate
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; 80-120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual; land user right - leased
Landuse Perennial; non-woody (herbaceous)
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of top soil; surface erosion
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Vegetative Measures; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Control of raindrop splash; control of dispersed runoff; retain/trap, impede/retard; control of concentrated runoff; retain/trap, impede/retard, drain/divert
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Bedding, harrowing, Mulching, Planting materials (pineapple); plowing, construction of vegetative strips (laid out during the land preparation). Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 6,720 P/ha; Equipment (machine use) - 10, 580/ P/ha; Agricultural inputs: planting materials (pineapple) - 10, 200 P/ha; Total Cost - 27, 205 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent cost: Labor - 13,100 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.80 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.33 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.70 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.40 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.23 Medium
-
Modified Rapid Composting
Modified Rapid Composting is the in situ decomposition of rice straw using compost fungus activator, Trichoderma harzianum or Effective Microorganism, help in utilizing the residual Nitrogen-Phosphorus-Potassium (NPK) from the decomposed rice straw.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform plateau/plains
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level >120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure individual; titled
Landuse Annual cropping; full irrigation
Land degradation Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Organic matter / soil fertility; Mitigation /ReductionTechnical function increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling); - increase in organic matter
Establishment input and cost per ha Maintenance and recurrent activties: Labor for spreading rice straws - 1,300P/ha/year; Spraying of effective microorganism solution - 700 P/ha-year; Total - 2,000P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.04 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.81 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.02 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.49 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.36 Medium
-
Compact Farming for Vegetables Production
Landusers are organized into a group or association to undertake jointly activities in the farm which include operation, input procurement, and marketing of produced crops.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500 - 1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform footslopes to hillslopes
Slope moderate to rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; medium
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5-1 ; 1- 2
Land tenure communal, organised
Landuse Annual cropping Mixed: Agroforestry (before) Cropland: Annual cropping (after) mixed rainfed - irrigated
Land degradation Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, acidification
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Organic matter / soil fertility; Mitgation/reductionTechnical function Increase in organic matter; increase in nutrient availability
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Clearing of the area. Establisment cost: 10,400 P/ha. Maintenance and recurrent activities: Plowing, harrowing, establishment of Plots, Organic Fertilizer Application; transplanting, watering spraying of botanical pesticide, and harvesting. Maintenance and recurrent costs: Labor - 11, 400 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seedlings and fertilizers) - 7,850 P/ha. Total - 19,290 P/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.14 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.77 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.55 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.12 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.58 Medium
-
Sweet Potato Relay Cropping
"Lapat System"
A farmer’s indigenous practice of growing sweet potato as a relay crop to its main crop of either rice or corn.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform hillslopes; mountain slopes
Slope rolling -hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50 -1
Land tenure Individual; mixed land ownership
Landuse Annual cropping; rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Biological degradation: reduction of vegetation cover
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Soil surface treatment Agronomic: Vegetation/soil cover; Mitigation/ReductionTechnical function control of raindrop splash - improvement of ground cover
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Agricultural inputs (corn seeds, rice seeds, sweet potato cuttings) - 5,100 P/ha; Maintenance and recurrent costs: clearing, plowing, harrowing, furrowing and planting of corn, rice and sweet potato. and spraying - 18,400 P/ha-year; Agricultural (insecticides) - 500 P/ha-year. Total 18,900 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.02 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.43 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.51 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
2.95 Negligible
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.91 Low
-
Organic-Based System of Rice Intensification (SRI)
Intensifying the irrigated rice production while at the same time reducing farm inputs including seeds, fertilizer, and water.
Location lowland; upland and hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100 ; 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform plateau/plains
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level >120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1 -2
Land tenure individual; titled
Landuse Annual cropping
Land degradation Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Management: Major change in timing of activities Agronomic: Organic matter / soil fertility. Prevention & Mitigation/reductionTechnical function increase in organic matter; increase / maintain water stored in soil
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Planting of rice seeds, raising of ducks. Establishment cost of inputs: Ducks - 8,300 P/ha; rice seeds - 900 P/ha. Total - 9,200 P/ha. Maintenance and recurrent activities: fertilizer application (compost); harvesting; weeding; first plowing; spraying of natural concoctions; organic fertilizer application; clearing; transplanting; second plowing. Maintenance and recurrent inputs and costs: Labor - 10,026 P/ha-year; Equipment - 6,200 P/ha-year; Fertilizers - 3,100 P/ha-year. Total - 19,326 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.99 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.75 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.02 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.63 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.39 Medium
-
Composting using Indigenous Microorganism (IMO)
Composting is the natural process of decomposition of organic matter by microorganisms under controlled conditions.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 1000-5000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform mountain slopes
Slope steep
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 0-20; medium
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5-1
Land tenure individual; titled
Landuse Annual cropping Perennial (non-woody) cropping Grazing land: Extensive grazing land (before) Cropland: Annual cropping (after) full irrigation
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Organic matter / soil fertility; Mitgation/reductionTechnical function Increase in organic matter; increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…); improvement of topsoil structure (compaction); increase of infiltration
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Inputs: Procurement of sprayer, shredder, seedling pots and trays; establishment of composite chamber (shed) - 115,500 P/unit. Maintenance and recurrent activities -Hauling of grass and weeds available in the farm; Shredding of grass and weeds; Spraying the shredded grass and weeds with indigenous microorganisms (IMO); Leave for 14 days to decompose; Application of Compost. Labor - 2,600P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.96 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.71 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.25 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.51 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.43 Medium
-
Organic Mulching
Organic mulching is a practice of applying thin layer of organic materials on the soil surface that decompose over time for the purpose of conserving soil moisture, reducing soil erosion, improving soil fertility, and reducing weed growth.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 1000-5000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform mountain slopes
Slope steep
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 0-20; medium
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5-1
Land tenure individual; titled
Landuse Annual cropping Perennial (non-woody) Grazing land: Extensive grazing land (before) Cropland: Annual cropping (after) full irrig
Land degradation Water degradation: aridification
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Soil surface treatment; Organic matter/ soil fertility; Vegetation/soil cover; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function control of raindrop splash ; improvement of ground cover; - increase in organic matter; increase / maintain water stored in soil
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment inputs: Shredder (Machine) - 104,400 P/unit; Sprayer - 1,000 P/unit. Maintenance/recurrent activities (hauling of grasses and weeds available in the farm, shredding of grasses and weeds, spreading of shredded grasses and weeds to the soil surface,spraying of IMO to the shredded grasses): Labor - 2,800 P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.00 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.54 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.21 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.30 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.05 Medium
-
Sugar Mill Wastewater Re-use for Irrigation
Re-using of wastewater to support agricultural crop production, as well as, to help in environmental protection
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform plateau/plain
Slope flat to gently sloping
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level
Land holding/hh (ha) 500-1000
Land tenure company
Landuse Annual Cropping; cropland
Land degradation Water degradation: decline of surface water quality
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural measures: sanitation/wastewater structures; management measures-waste managementTechnical function Conserve ecosystem; protect wateshed/downstream areas
Establishment input and cost per ha Not available
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.00 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.00 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.50 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
4.00 High
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.50 Medium
-
Highly Diversified Cropping in Live Trellis System
"Kakawate as live trellis "balag""
Gliricidia sepium locally known as "kakawate" served as live trellis / or anchorage for annual crops (mostly creeping-type vegetables) and erosion control measure. The technology is well-adopted in the community providing immediate food for the farmers and increased income due to diversified farming.
Location upland to hillyland; highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000 -2000
Landform footslopes and mountainslopes
Slope hilly to rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 51-80; moderately deep; medium to high fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5 - 1.0
Land tenure individual
Landuse Annual cropping: cropland; Mixed (crops/grazing) incl agroforestry
Land degradation Soil erosio by water: loss of topsoil/surface erosion; offsite degradation effects
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic measures - Vegetation/ soil cover, Organic matter/ soil fertility, : Soil surface treatment. Vegetative measures - V1: Tree and shrub coverTechnical function Improve production; prevent and reduce land degradation; preserve and improve biodiversity
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Manual labor for weeding, planting, fertilizer applicatio, harvesting and hauling - P3,600/ha; Planting materials - P2,550/ha; Fertilizers and biocides - P10,030/ha; Construction materials - P3,880; Total cost - P20, 060. Maintenance activities: Labor for weeding, trimming of kakawate, application of ferilizers, spraying - P4,500/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.20 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.50 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.00 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.50 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.20 Medium
-
Mangroves as Buffer against Natural Hazards
"Bakauan"
Mangroves "bakauan" are planted in the island coast to form barriers and as first line of defense during storm surges.
Location coastal area
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 0.00- 100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1,500 - 2,000
Landform Coast
Slope 0-2
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level Low
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5 - 1.0
Land tenure State
Landuse Forest/woodlands; crustaceans breeding ground
Land degradation Reduction of vegetation cover; loss of habitats
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetatative measures; prevent land degradationTechnical function Conserve ecosystem; preserve improve biodiversity; reduce disaster; adapt to CC; mitigate CC
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Labor - P2500/ha; Planting materials - P5000/ha; Total Cost -P7500. Maintenance and Recurrent Activities: Labor - P750/ha; Replanting materials - P250/ha; Total - P1,000/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.60 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.50 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.50 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
4.00 High
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.60 Medium
- All
- Agronomic
- Vegetative
- Structural
- Management
- Agronomic and Vegetative
- Other combination of measures
-
Conservation Tillage Practices for Corn Production
"Tipid Saka"
A crop production system which focuses on soil conservation and reducing excessive tillage operations, reduces labor and farm inputs while increasing productivity and profitability.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform plains
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure untitledland (leased)
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Chemical Soil Deterioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic measures: Prevention and mitigation/reductionTechnical function increased soil fertility and good soil structure for better nutrient and water uptake by plants
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment input and cost per ha: Labor - 6,950 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seeds, fertilizer, biocides, Bio-N) - 4,400 P/ha; Others (post harvest, market transport and packaging) - 10,810 P/ha. Total Cost - 22,160 P/ha.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.83 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.67 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.84 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.52 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.86 Medium
-
Natural Vegetative Strips (NVS)
Within individual cropland plots, strips of land are marked out on the contour and left unploughed in order to form permanent, cross-slope barriers of naturally established grasses and herbs.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500 -1500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-3000
Landform footslopes; hillslopes
Slope rolling-hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-80; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-20
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, trees and shrubs: rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of top soil; surface erosion; gully erosion; chemical soil deterioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter.
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Vegetative Measures; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Reduction of slope angle; reduction of slope length; control of dispersed runoff; increase infiltration and increase soil fertility
Establishment input and cost per ha Establisment activities: Lay out of contour using A-frame; placing wooden pegs along contours; seeding; transplanting; land preparation. Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 1000 P/ha; Equiipment (animal traction, tools, and stakes) - 3,300 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seeds, seedlings, fertilizer, biocides) - 9,000 P/ha; Total Cost - 13,300 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Plowing along the contour leaving unplowed strips; planting; mulching; fertilization, interim cultivation/weeding; plowing mulch into the soil; weeding slashing grass; spreading the cut materials evenly in the alleys; pruning. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and cost per ha per year: Labor -1,700 P/ha-year; Equipment (animal traction, tools) - 1,980 P/ha-year; Agricultural inputs (seeds, fertilizer, biocides) - 7,500 P/ha-year; Total maintenance cost - 11,180 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.81 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.56 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.95 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.63 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.95 Medium
-
In 'situ' Decomposition of Banana Stalk
"Palata System"
Leaving the trunk of a newly harvested banana standing beside a follower plant to provide nutrients and moisture especially during period of drought.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) < 100
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform plateau/plains
Slope flat-gently sloping
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level >120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 2-5; 500-1,000
Land tenure company leased
Landuse Perennial (non-woody) cropping, full irrigation
Land degradation Chemical soil detrioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, water degradation; aridification
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic Measures: Mitigation/reduction and rehabilitationTechnical function Increase soil fertility; Increase/maintain water stored in the soil
Establishment input and cost per ha Maintenance/recurrent activities: 1) Cutting of crown of newly harvested plants; Inputs: Labor - 2,350 P/ha-year; Equipment - cutting tools - 500 P/ha-year; Total Cost - 2,850P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.63 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.02 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.65 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
2.99 Negligible
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.29 Low
-
Small Water Impounding Project (SWIP)
Development of micro-catchment for soil and water conservation and for the provision of supplementary irrigation during the dry season.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-3000
Landform hillslopes; valley
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 80-120 ; >120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping; perennial crop
Land degradation Water degradation, aridification
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures; Mitigation/reduction and rehabilitationTechnical function Water harvesting nd increase water supply
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Clearing, staking and laying out; Stripping and excavation; embankment filling; pipe lay out and installation; riprapping; concrete works, embankment sodding; and canal excavation and lining. Establishment inputs and cost per ha of service area: Labor - 105,000 P/ha; Materials - 99,000 P/ha; 96,000 P/ha; Total Cost - 300,000 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent costs (Embankment maintenance, appurtenant structures maintenance, canal maintenance): Labor - 12,000 P/ha-year; Minor equipment - 3,000 P/ha-year; Total maintenance cost - 15,000 P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.26 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.62 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.05 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
4.04 High
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.97 High
-
Small Farm Reservoir (SFR)
"Tabon"
The Small Farm Rerservoir is an earth dam structure used to trap harvest and store rainfall and water runoff.
Location lowland; upland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) < 100; 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform plains/hillslopes
Slope rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; low organic matter content
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping
Land degradation soil erosion and excessive runoff; limited water supply
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures: Prevention and rhabilitationTechnical function Water harvesting/ increase water supply; Control dispersed runoff, retain/trapped; contol concentrated runoff: retain/trap.
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: 1) Laying-out & staking; 2) Clearing; 3) Excavation; 4) Spreading of fill materials; 5) Embankment filling and compaction; 6) pipe laying out and setting; and 7) canal/spillway construction. Total construction cost - 40,000 - 100,000 P/unit.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.03 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.40 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.96 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.97 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.36 Medium
-
Multi-Storey Cropping
"Maramihang Pagtatanim or Planting in Great Numbers"
Cultivating a mixture of crops with different heights (multi-storey) and growth characteristics which together optimise the use of soil, moisture and space.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform footslopes, ridges, and plateau/plain
Slope gentle - moderate
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 80-120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Agroforestry, rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of top soil/surface runoff; chemical soil deterioration; fertilit decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Vegetative Measures; PreventionTechnical function Control raindrop splash; improvement of ground cover
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment actvities: Planting of tallest storey (coconut); Planting of lowest storey (pineapple); Planting of lowest storey continued (root crops); Planting of middle storey (coffe and banana). Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 7,000 P/ha; Equipment (animal traction and farm tools) - 4, 230 P/ha; Agricultural (seedlings, fertilizer, biocides, compost/manure) - 54,000 P/ha; Total Cost - 65,230 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha per year: Labor - 14,100 P/ha-year; Agricultural (fertilizer, biocides) - 9,000 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.40 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.97 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.21 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.98 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 16.56 High
-
Residue Incorporation (Corn)
"Palugdang", "Palata"
Incorporation of corn stalks during land preparation for the succeeding crop.
Location upland to hillyland and highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-1500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-3000
Landform footslopes- hillslopes; plateau/plains
Slope gentle-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50 - > 120 ; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-5
Land tenure titled, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline; and reduced organic matter content
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic Measures: RehabilitationTechnical function Increase soil fertility and organic matter
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Equiipment (animal traction) - 1,500 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seeds, fertilizer, biocides) - 7,700 P/ha; Others (planting, Harvesting, Maintenance) - 4,500 P/ha; Total cost - 13,700 P/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.56 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.04 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.98 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.16 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.74 Low
-
Planted Vegetative Strips (PVS)
Planting of economic crops/forages in strips along the contour to control soil loss through erosion.
Location lowland; upland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100; 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-2000
Landform hillslopes; plateaus/plains
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of top soil; surface erosion
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic Measures; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Control; dispersed runoff; imped and retard
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Planting of Alley crops; contouring; planting of vegetative strips. Establishment inputs and costs: Labor - 950 P/ha; Equipment (animal traction) - 600 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seeds and seedlings) - 5,300 P/ha. Total Cost - 6,850 P/ha.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.81 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.69 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.94 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.53 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.97 Medium
-
Windbreaks
Planting of herbaceous plants or trees along property boundaries to serve as windbreaks and as sources of fodder and fuel.
Location lowland; upland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) < 100; 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform footslopes; hillslopes
Slope rolling-hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level > 120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse agro-silvo pastoralism, rainfed
Land degradation soil erosion by wind, loss of top soil
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; PreventionTechnical function Reduction in wind speed
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment inputs and cost per ha (seeding /planting): Labor - 1,880 P/ha'; Tools - 250 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seedling, stem cuttings) - 800 P/ha. Total Cost - 2,930 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Removal of dead branches (trees); Cutting of grasses. Maintenance/recurrent cost per ha per year: Labor - 700 P/ha-year; Minor tools - 300 P/ha; Total recurrent cost - 1,000 P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.57 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.44 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.66 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.32 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.99 Low
-
Rainfed paddy rice terraces
"Palayan"
Terraces supporting rainfed paddy rice on steep mountain slopes: these have been in existence for more than a thousand years.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 1500-2500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-3000
Landform mountain slopes
Slope hilly - steep
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 80-120; > 120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha)
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of topsoil/surface erosion; chemical soil deterioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures (Bench Terraces); Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Control of dispersed runoff: retain trap; increase/maintain water stored in the soil; reduction of slope angle; reduction of slope length; indirect maintenance of fertility
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Levelling by moving soil from upslope to the downslope part; construction of bunds (lip at the terrace ridge) of about 50-100 cm; determination of contour lines. Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 115,000 P/ha; Equipment - 10,000 P/ha; Total cost - 125,000 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Weeding by cutting grasses on the bund/riser using hand tools, hoeing; Land preparation by puddling, in most cases the use of animal traction is not possible because of the steepness of the slope and height of the risers; Repairing breached portion of the bunds, adding few centimeters in the process. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha per year: Labor - 3,000 P/ha-year; Equipment (farm tools) - 1000 P/ha-year; Total maintenance cost - 4,000 P/ha-year. Remarks: The costs of establishment are just estimates as new terrace construction no longer takes place in the study area. The land has already been terraced for centuries. The maintenance costs assumes minor and light maintenance and does not include major repairs of bunds.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.91 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.67 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.93 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.69 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.20 Medium
-
Stone bunds and small basins
"Pamugong sa yuta (Cebuano)"
Piling of stones and rocks along the contour to control run-off and soil erosion. It is also about the creation of small basins by removing stones and using them as barriers.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1,500-2,000
Landform hill slopes
Slope rolling - hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level > 120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Surface soil erosion, top soil removal
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures; Mitigation and rehabilitationTechnical function control of concentrated runoff; retain/trap
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Contouring; gathering and piling of stones along contour with development of small basin for rainwater impoundment. Establishment inputs and cost per ha. Labor - 47,000 P/ha; Equipment - 1,000 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 1,800 P/ha.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.46 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.15 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.50 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.47 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.58 Low
-
Vetiver grass system or Vetiver grass technology
"Mora, Moras, Amora and Modas in the different regions in the Philippines"
Vetiver grass used as contour hedgerows in sloping agricultural land used for annual crops.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform hillslopes
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80 ; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping rainfed
Land degradation Surface erosion by water, loss of top soil
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; Mtigation and preventionTechnical function control dispersed runoff, retain top soil; reduction of slope length
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Planting vertiver grass along contour; Replacement/replanting gaps. Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 2,350 P/ha; Seedlings - 4,700 P/ha; Total Cost - 7,050 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Pruning. Maintenance and recurrent inputs and cost per ha per year: Labor - 1,000 P/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.38 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.14 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.77 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.51 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.80 Low
-
Littuko Growing for Forest Enhancement
Growing of rattan is done by upland farmers as part of the Community Based Forest Management (CBFM).
Location upland to hillyland and higland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500; 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform hillslopes
Slope hilly to steep
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50-1
Land tenure communal, organized
Landuse Natural;; Other: Grazing land; forest
Land degradation Biological degradation: reduction of vegetation cover; loss of habitat
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; RehabilitationTechnical function Promotion of vegetation species and varieties; conservation of trees that serve as hosts; increase organic matter; increase biomass
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Nursery establishment through seedbed; transplanting. Establishment per unit: Labor - 400 P/unit; Agricultural inputs (incl. seeds) - 10,400 P/ha; Total Cost -10,800/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.65 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.48 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.93 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.39 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.45 Medium
-
Rockwall Terracing
Rockwall terracing refers to the piling of stones or rocks along contour lines to reduce soil erosion in hilly areas.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform hillslopes-mountain slopes
Slope rolling - hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure not titled, individual
Landuse Annual cropping; mixed grazing land, rainfed and irrigated
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of topsoil/surface runoff
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Strucutural Measures; RehabilitationTechnical function control of dispersed runoff: retain trap; retain /trap; control concentrated runoff: retain trap; control soil erosion
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Contouring; Digging along contour; Gathering and piling of stones along contour. Establishment inpputs and costs per unit (ha): Labor - 37,800 P/ha; Equipment - 1,000 P/ha; Total cost - 38,800 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent of activities: Re-piling of stones and rocks that are dislodged. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per unit (ha) per year: Labor - 1,000 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.30 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.19 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.66 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.28 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.43 Low
-
Seed Production of Multipurpose Shrubs/Legumes
Seed production of multipurpose shrubs and legumes, a soil conservation practice in sloping areas wherein flemingia (Flemingia macrophylla) and Indigofera (Indigofera tinctoria) are densely planted along contours.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform hillslopes-mountainslopes
Slope rolling-hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50-1
Land tenure titled, individual
Landuse Trees and shrubs cropping: Forests/woodlands: natural cropland
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of topsoil/ surface runoff; chemical deterioraton-fertlity decline; biological degradation
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; RehabilitationTechnical function control of dispersed runoff-retain/trap; control of concentrated runoff; retain/trap; improvement of ground cover; promotion of vegetation species and varieties
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Land preparation; Plowing, harrowing and furrowing; Establishment of contour lines and laying out. Establishment inputs and costs per unit (ha): Labor - 2,300 P/ha; Equipment (bamboo pegs) - 150 P/ha; Seeds - 2,100 P/ha; Total Cost - 4,550 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Weeding/hilling-up; Harvesting; Sun drying; Manual threshing; Harvesting of Flemengia and Indigofera. Maintenance/recurrent costs: Labor - 2,100 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.06 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.47 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.95 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.41 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.89 Medium
-
Contour Farming Using Hedgerows
"Contour Farming"
Contour farming is a technology practiced in sloping areas in which hedgerows are established along the contours and other annual/cash crops are grown in the alleys between the hedges.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform hillslopes-mountain slopes
Slope rolling - hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) < 0.50
Land tenure not titled, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of topsoil/ surface erosion; chemical deterioration; fertillity decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Vegetative Measures; RehabilitationTechnical function Conrol of dispersed runoff: retain/trap; minimize soil erosion due to runoff; serve as soil nutrient traps
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Laying out and establishment of contour lines/hedges; Planting of hedgerows with Napier grass; Planting of perennial crops along contour. Establishment inputs and costs per unit (ha): Labor - 1,350 P/ha; Local materials (A-frame) - 100 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seedlings, herbecides) - 4,400 P/ha; Total cost - 5,850 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Land preparation of alley between hedges; furrowing; planting of corn (first cropping); Weeding; Harvesting of first crop; Planting of second crop (corn & peanut; Weeding; Harvesting of second crop. Maitenance/recurrent inputs and cost per ha per year: Labor - 1,950 P/ha-year; Equipment (animal traction)/ - 300 P/ha-year; Agricultural inputs (seeds and fertilizer) - 2,200 P/ha-year: Total maintenance cost - 4,450 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.03 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.76 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.08 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.90 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.77 High
-
Vegetable Terracing
Vegetable terracing is a technology practiced at which point terraces are established from the contours along mountain slope for crop production.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 2000-2500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform hillslopes-mountainslopes
Slope rolling-hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50;low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50-1
Land tenure titled, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, Forest/woodlandrest/woodlands
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of topsoil/surface erosion; chemical soil deterioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Structural Measures; Mitigation/ReductionTechnical function Control of dspersed runoff: impede/retart; control concentrated runoff: impede/retard; reduction of slope angle
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Establishment of terraces. Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 25,100 P/ha; Minor tools - 600 P/ha; Total cost - 25,700 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Land preparation; application of chicken manure; Planting; hilling up including application of fertilizer; Weeding; Spraying of insecticides; Harvesting. Maintenance/recurrent costs per ha per year: Labor - 14,570 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (fertilizer, compost/manure, insecticides) - 43,300 P/ha-year. Total maintenance/recurrent costs - 57,870 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.16 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.88 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.82 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.56 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.42 Medium
-
Alternate Wetting and Drying
Alternate Wetting and Drying is a water-use management technique wherein irrigation water input could be substantially reduced to as much as 35% without significantly affecting rice yields.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) < 100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform plain
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level > 120 ; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50-1
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual Cropping, irrigated
Land degradation Water degradation, change in quantity of surface water
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Management Measures- Major changes in timing of activities; PreventionTechnical function More efficient water use
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: 1) Preparation of PVC/bamboo tubes; 2) Perforating the sides of the tubes with many holes; Establishment inputs and cost per unit: Labor - 160 P/pc; Materials: PVC - 210 P/pc; Total Cost - 370P/pc
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.88 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.33 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.92 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.59 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.72 Medium
-
Trees as Buffer Zones
Trees as buffer zones are vegetative measures established in the area to prevent pest from crossing in between blocks. Further, the technology provides haven for flora and fauna which are endemic in the area.
Location upland to hillyland; highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500; 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform hillslopes; valley
Slope gentle - moderate
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; 80-120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Trees and shrubs
Land degradation Biological degradation; loss of habitats
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; Mitigation and preventionTechnical function Control of raindrop splash; control of dispersed runoff; stabilization of soil; reduction in wind speed; increase biomass; spatial arrangement and diversification of land use; improve biodiversity
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Grass Brushing; Hole Digging; Planting. Establishment inputs: Labor - 5,500 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent cost per hac per year: Labor - 3,700 P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.80 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.63 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.08 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.66 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.17 Medium
-
Pressing of Cogon Grass (Imperata cylindrica)
An indigenous technology of enhancing wildling growth by pressing of cogon grass.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform hillslopes; mountain slopes
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 50-100
Land tenure Lands owned by the state; Land user rights: open access (unorganized)
Landuse Natural; Deforested Land
Land degradation Biological degradation; loss of habitats
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures, Others (Suppressing of Cogon; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Enhance the growth of wildling by controlling the growth of fast-growing grasses (cogon); control/avoid forest fires
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Identification of wildlings (2 feet high); Ring weeding; Pressing of cogon away from wildlings; Application of fertilizers. Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 950 P/ha; Construction material (wood and rope) - 200 P/ha; Total Cost - P 1,150 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Pressing of Cogon (Labor) - 210 P/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 2.68 Negligible
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
2.52 Negligible
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.22 Low
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
2.67 Negligible
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 11.09 Low
-
Firebreaks/Greenbreaks
Gaps in vegetation or other combustible material that act as barriers to prevent and/ or control the spreading of forest fires to other areas.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform hillslopes; mountain slopes
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 50-100
Land tenure Lands owned by the state; Land user rights: open access (unorganized)
Landuse Plantation; afforestation, tree generation
Land degradation Biological degradation; detrimental effects of fire
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures, Others (Suppressing of Cogon; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Control fires; reduction of dry materials (fuel for wildfires)
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Clearing of Cogon in the firelines; Planting of kakawate cuttings. Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 1,250 P/ha. Maintenance: 500 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.11 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.16 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.86 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.36 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.49 Low
-
Ecological engineering for irrigated lowland rice ecosystem
Ecological engineering for lowland rice ecosystem by promoting and planting of flower strips in rice fields.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform plateau/plains
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 0-20; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5-1
Land tenure titled land, individual; water use rights- communal (organised)
Landuse Annual cropping, full irrigation
Land degradation Biological degradation: increase of pests/diseases, lost of predators
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; Others (Annual Flower Strips; Prevention and Mitigation/ReductionTechnical function Biological control reduces pollution by agro-chemicals
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Flowering plant seed collection; flowering plant nursery establishment; transplanting flowering plants. Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 4,730P/ha; Agricultural inputs (fertilizer, compost/manure - 1,600 P/ha; Total Cost - 6,330 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Flowering plant maintenance, i.e. trimming, removal of volunteer seedlings out of the strips and thinning during cropping season; Watering and replacement in times of long drought fallow period. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha per year: Labor - 1,880 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.08 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.87 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.05 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.64 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.64 High
-
Sediment Traps
"Catch basin, silt traps, cascading canals, trenches, ditches"
Sediment traps are structures built in the area which includes cascading catchment canal, silt traps and catch basin along perimeter, between pineapple fields and along diversion ditches to collect run-off during rains, preventing and minimizing the eroded soils cascading into natural bodies of water.
Location upland to hillyland; highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500; 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform hillslopes; valley floors
Slope gentle - moderate
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; 80-120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual; land user right - leased
Landuse Perennial; non-woody: Other: waterways, drainage lines, ponds, dams (after)
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of top soil; surface erosion
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures (Cascading canals and Silt Traps); Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Sediment retention/trapping, sediment harvesting; Control of dispersed runoff; retain/trap, impede/retard; control of concentrated runoff; retain/trap, impede/retard, drain/divert.
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activiteis: Excavation of canal; construction of bed; constructiobn of trenches. Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 2,530 P/ha; Equipment - 3,360 P/ha. Maintenance activities: Desilting. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha: Labor - P7,300 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.33 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.12 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.79 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.60 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.84 Low
-
Contour Straight Block Layout
It is a package of soil and water conservation technology that integrates contouring, bedding, and blocking.
Location upland to hillyland; highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500; 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform hillslopes; valley
Slope gentle - moderate
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; 80-120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual; land user right - leased
Landuse Perennial; non-woody (herbaceous)
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of top soil; surface erosion
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Vegetative Measures; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Control of raindrop splash; control of dispersed runoff; retain/trap, impede/retard; control of concentrated runoff; retain/trap, impede/retard, drain/divert
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Bedding, harrowing, Mulching, Planting materials (pineapple); plowing, construction of vegetative strips (laid out during the land preparation). Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 6,720 P/ha; Equipment (machine use) - 10, 580/ P/ha; Agricultural inputs: planting materials (pineapple) - 10, 200 P/ha; Total Cost - 27, 205 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent cost: Labor - 13,100 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.80 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.33 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.70 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.40 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.23 Medium
-
Modified Rapid Composting
Modified Rapid Composting is the in situ decomposition of rice straw using compost fungus activator, Trichoderma harzianum or Effective Microorganism, help in utilizing the residual Nitrogen-Phosphorus-Potassium (NPK) from the decomposed rice straw.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform plateau/plains
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level >120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure individual; titled
Landuse Annual cropping; full irrigation
Land degradation Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Organic matter / soil fertility; Mitigation /ReductionTechnical function increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling); - increase in organic matter
Establishment input and cost per ha Maintenance and recurrent activties: Labor for spreading rice straws - 1,300P/ha/year; Spraying of effective microorganism solution - 700 P/ha-year; Total - 2,000P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.04 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.81 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.02 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.49 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.36 Medium
-
Compact Farming for Vegetables Production
Landusers are organized into a group or association to undertake jointly activities in the farm which include operation, input procurement, and marketing of produced crops.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500 - 1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform footslopes to hillslopes
Slope moderate to rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; medium
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5-1 ; 1- 2
Land tenure communal, organised
Landuse Annual cropping Mixed: Agroforestry (before) Cropland: Annual cropping (after) mixed rainfed - irrigated
Land degradation Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, acidification
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Organic matter / soil fertility; Mitgation/reductionTechnical function Increase in organic matter; increase in nutrient availability
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Clearing of the area. Establisment cost: 10,400 P/ha. Maintenance and recurrent activities: Plowing, harrowing, establishment of Plots, Organic Fertilizer Application; transplanting, watering spraying of botanical pesticide, and harvesting. Maintenance and recurrent costs: Labor - 11, 400 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seedlings and fertilizers) - 7,850 P/ha. Total - 19,290 P/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.14 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.77 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.55 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.12 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.58 Medium
-
Sweet Potato Relay Cropping
"Lapat System"
A farmer’s indigenous practice of growing sweet potato as a relay crop to its main crop of either rice or corn.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform hillslopes; mountain slopes
Slope rolling -hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50 -1
Land tenure Individual; mixed land ownership
Landuse Annual cropping; rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Biological degradation: reduction of vegetation cover
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Soil surface treatment Agronomic: Vegetation/soil cover; Mitigation/ReductionTechnical function control of raindrop splash - improvement of ground cover
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Agricultural inputs (corn seeds, rice seeds, sweet potato cuttings) - 5,100 P/ha; Maintenance and recurrent costs: clearing, plowing, harrowing, furrowing and planting of corn, rice and sweet potato. and spraying - 18,400 P/ha-year; Agricultural (insecticides) - 500 P/ha-year. Total 18,900 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.02 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.43 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.51 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
2.95 Negligible
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.91 Low
-
Organic-Based System of Rice Intensification (SRI)
Intensifying the irrigated rice production while at the same time reducing farm inputs including seeds, fertilizer, and water.
Location lowland; upland and hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100 ; 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform plateau/plains
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level >120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1 -2
Land tenure individual; titled
Landuse Annual cropping
Land degradation Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Management: Major change in timing of activities Agronomic: Organic matter / soil fertility. Prevention & Mitigation/reductionTechnical function increase in organic matter; increase / maintain water stored in soil
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Planting of rice seeds, raising of ducks. Establishment cost of inputs: Ducks - 8,300 P/ha; rice seeds - 900 P/ha. Total - 9,200 P/ha. Maintenance and recurrent activities: fertilizer application (compost); harvesting; weeding; first plowing; spraying of natural concoctions; organic fertilizer application; clearing; transplanting; second plowing. Maintenance and recurrent inputs and costs: Labor - 10,026 P/ha-year; Equipment - 6,200 P/ha-year; Fertilizers - 3,100 P/ha-year. Total - 19,326 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.99 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.75 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.02 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.63 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.39 Medium
-
Composting using Indigenous Microorganism (IMO)
Composting is the natural process of decomposition of organic matter by microorganisms under controlled conditions.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 1000-5000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform mountain slopes
Slope steep
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 0-20; medium
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5-1
Land tenure individual; titled
Landuse Annual cropping Perennial (non-woody) cropping Grazing land: Extensive grazing land (before) Cropland: Annual cropping (after) full irrigation
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Organic matter / soil fertility; Mitgation/reductionTechnical function Increase in organic matter; increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…); improvement of topsoil structure (compaction); increase of infiltration
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Inputs: Procurement of sprayer, shredder, seedling pots and trays; establishment of composite chamber (shed) - 115,500 P/unit. Maintenance and recurrent activities -Hauling of grass and weeds available in the farm; Shredding of grass and weeds; Spraying the shredded grass and weeds with indigenous microorganisms (IMO); Leave for 14 days to decompose; Application of Compost. Labor - 2,600P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.96 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.71 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.25 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.51 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.43 Medium
-
Organic Mulching
Organic mulching is a practice of applying thin layer of organic materials on the soil surface that decompose over time for the purpose of conserving soil moisture, reducing soil erosion, improving soil fertility, and reducing weed growth.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 1000-5000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform mountain slopes
Slope steep
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 0-20; medium
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5-1
Land tenure individual; titled
Landuse Annual cropping Perennial (non-woody) Grazing land: Extensive grazing land (before) Cropland: Annual cropping (after) full irrig
Land degradation Water degradation: aridification
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Soil surface treatment; Organic matter/ soil fertility; Vegetation/soil cover; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function control of raindrop splash ; improvement of ground cover; - increase in organic matter; increase / maintain water stored in soil
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment inputs: Shredder (Machine) - 104,400 P/unit; Sprayer - 1,000 P/unit. Maintenance/recurrent activities (hauling of grasses and weeds available in the farm, shredding of grasses and weeds, spreading of shredded grasses and weeds to the soil surface,spraying of IMO to the shredded grasses): Labor - 2,800 P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.00 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.54 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.21 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.30 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.05 Medium
-
Sugar Mill Wastewater Re-use for Irrigation
Re-using of wastewater to support agricultural crop production, as well as, to help in environmental protection
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform plateau/plain
Slope flat to gently sloping
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level
Land holding/hh (ha) 500-1000
Land tenure company
Landuse Annual Cropping; cropland
Land degradation Water degradation: decline of surface water quality
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural measures: sanitation/wastewater structures; management measures-waste managementTechnical function Conserve ecosystem; protect wateshed/downstream areas
Establishment input and cost per ha Not available
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.00 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.00 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.50 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
4.00 High
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.50 Medium
-
Highly Diversified Cropping in Live Trellis System
"Kakawate as live trellis "balag""
Gliricidia sepium locally known as "kakawate" served as live trellis / or anchorage for annual crops (mostly creeping-type vegetables) and erosion control measure. The technology is well-adopted in the community providing immediate food for the farmers and increased income due to diversified farming.
Location upland to hillyland; highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000 -2000
Landform footslopes and mountainslopes
Slope hilly to rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 51-80; moderately deep; medium to high fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5 - 1.0
Land tenure individual
Landuse Annual cropping: cropland; Mixed (crops/grazing) incl agroforestry
Land degradation Soil erosio by water: loss of topsoil/surface erosion; offsite degradation effects
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic measures - Vegetation/ soil cover, Organic matter/ soil fertility, : Soil surface treatment. Vegetative measures - V1: Tree and shrub coverTechnical function Improve production; prevent and reduce land degradation; preserve and improve biodiversity
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Manual labor for weeding, planting, fertilizer applicatio, harvesting and hauling - P3,600/ha; Planting materials - P2,550/ha; Fertilizers and biocides - P10,030/ha; Construction materials - P3,880; Total cost - P20, 060. Maintenance activities: Labor for weeding, trimming of kakawate, application of ferilizers, spraying - P4,500/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.20 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.50 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.00 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.50 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.20 Medium
-
Mangroves as Buffer against Natural Hazards
"Bakauan"
Mangroves "bakauan" are planted in the island coast to form barriers and as first line of defense during storm surges.
Location coastal area
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 0.00- 100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1,500 - 2,000
Landform Coast
Slope 0-2
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level Low
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5 - 1.0
Land tenure State
Landuse Forest/woodlands; crustaceans breeding ground
Land degradation Reduction of vegetation cover; loss of habitats
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetatative measures; prevent land degradationTechnical function Conserve ecosystem; preserve improve biodiversity; reduce disaster; adapt to CC; mitigate CC
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Labor - P2500/ha; Planting materials - P5000/ha; Total Cost -P7500. Maintenance and Recurrent Activities: Labor - P750/ha; Replanting materials - P250/ha; Total - P1,000/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.60 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.50 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.50 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
4.00 High
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.60 Medium
- All
- Soil Fertility Management
- Water Management
- Runoff Management and Erosion Control (Structural)
- Runoff Management and Erosion Control (Vegetative)
- Enrichment and Protection of Vegetative Cover
- Fire and Wind Breaks
- Biological Pest Control
- Others
-
Conservation Tillage Practices for Corn Production
"Tipid Saka"
A crop production system which focuses on soil conservation and reducing excessive tillage operations, reduces labor and farm inputs while increasing productivity and profitability.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform plains
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure untitledland (leased)
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Chemical Soil Deterioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic measures: Prevention and mitigation/reductionTechnical function increased soil fertility and good soil structure for better nutrient and water uptake by plants
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment input and cost per ha: Labor - 6,950 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seeds, fertilizer, biocides, Bio-N) - 4,400 P/ha; Others (post harvest, market transport and packaging) - 10,810 P/ha. Total Cost - 22,160 P/ha.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.83 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.67 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.84 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.52 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.86 Medium
-
Natural Vegetative Strips (NVS)
Within individual cropland plots, strips of land are marked out on the contour and left unploughed in order to form permanent, cross-slope barriers of naturally established grasses and herbs.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500 -1500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-3000
Landform footslopes; hillslopes
Slope rolling-hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-80; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-20
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, trees and shrubs: rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of top soil; surface erosion; gully erosion; chemical soil deterioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter.
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Vegetative Measures; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Reduction of slope angle; reduction of slope length; control of dispersed runoff; increase infiltration and increase soil fertility
Establishment input and cost per ha Establisment activities: Lay out of contour using A-frame; placing wooden pegs along contours; seeding; transplanting; land preparation. Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 1000 P/ha; Equiipment (animal traction, tools, and stakes) - 3,300 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seeds, seedlings, fertilizer, biocides) - 9,000 P/ha; Total Cost - 13,300 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Plowing along the contour leaving unplowed strips; planting; mulching; fertilization, interim cultivation/weeding; plowing mulch into the soil; weeding slashing grass; spreading the cut materials evenly in the alleys; pruning. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and cost per ha per year: Labor -1,700 P/ha-year; Equipment (animal traction, tools) - 1,980 P/ha-year; Agricultural inputs (seeds, fertilizer, biocides) - 7,500 P/ha-year; Total maintenance cost - 11,180 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.81 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.56 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.95 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.63 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.95 Medium
-
In 'situ' Decomposition of Banana Stalk
"Palata System"
Leaving the trunk of a newly harvested banana standing beside a follower plant to provide nutrients and moisture especially during period of drought.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) < 100
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform plateau/plains
Slope flat-gently sloping
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level >120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 2-5; 500-1,000
Land tenure company leased
Landuse Perennial (non-woody) cropping, full irrigation
Land degradation Chemical soil detrioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, water degradation; aridification
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic Measures: Mitigation/reduction and rehabilitationTechnical function Increase soil fertility; Increase/maintain water stored in the soil
Establishment input and cost per ha Maintenance/recurrent activities: 1) Cutting of crown of newly harvested plants; Inputs: Labor - 2,350 P/ha-year; Equipment - cutting tools - 500 P/ha-year; Total Cost - 2,850P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.63 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.02 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.65 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
2.99 Negligible
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.29 Low
-
Small Water Impounding Project (SWIP)
Development of micro-catchment for soil and water conservation and for the provision of supplementary irrigation during the dry season.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-3000
Landform hillslopes; valley
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 80-120 ; >120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping; perennial crop
Land degradation Water degradation, aridification
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures; Mitigation/reduction and rehabilitationTechnical function Water harvesting nd increase water supply
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Clearing, staking and laying out; Stripping and excavation; embankment filling; pipe lay out and installation; riprapping; concrete works, embankment sodding; and canal excavation and lining. Establishment inputs and cost per ha of service area: Labor - 105,000 P/ha; Materials - 99,000 P/ha; 96,000 P/ha; Total Cost - 300,000 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent costs (Embankment maintenance, appurtenant structures maintenance, canal maintenance): Labor - 12,000 P/ha-year; Minor equipment - 3,000 P/ha-year; Total maintenance cost - 15,000 P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.26 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.62 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.05 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
4.04 High
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.97 High
-
Small Farm Reservoir (SFR)
"Tabon"
The Small Farm Rerservoir is an earth dam structure used to trap harvest and store rainfall and water runoff.
Location lowland; upland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) < 100; 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform plains/hillslopes
Slope rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; low organic matter content
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping
Land degradation soil erosion and excessive runoff; limited water supply
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures: Prevention and rhabilitationTechnical function Water harvesting/ increase water supply; Control dispersed runoff, retain/trapped; contol concentrated runoff: retain/trap.
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: 1) Laying-out & staking; 2) Clearing; 3) Excavation; 4) Spreading of fill materials; 5) Embankment filling and compaction; 6) pipe laying out and setting; and 7) canal/spillway construction. Total construction cost - 40,000 - 100,000 P/unit.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.03 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.40 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.96 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.97 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.36 Medium
-
Multi-Storey Cropping
"Maramihang Pagtatanim or Planting in Great Numbers"
Cultivating a mixture of crops with different heights (multi-storey) and growth characteristics which together optimise the use of soil, moisture and space.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform footslopes, ridges, and plateau/plain
Slope gentle - moderate
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 80-120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Agroforestry, rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of top soil/surface runoff; chemical soil deterioration; fertilit decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Vegetative Measures; PreventionTechnical function Control raindrop splash; improvement of ground cover
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment actvities: Planting of tallest storey (coconut); Planting of lowest storey (pineapple); Planting of lowest storey continued (root crops); Planting of middle storey (coffe and banana). Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 7,000 P/ha; Equipment (animal traction and farm tools) - 4, 230 P/ha; Agricultural (seedlings, fertilizer, biocides, compost/manure) - 54,000 P/ha; Total Cost - 65,230 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha per year: Labor - 14,100 P/ha-year; Agricultural (fertilizer, biocides) - 9,000 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.40 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.97 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.21 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.98 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 16.56 High
-
Residue Incorporation (Corn)
"Palugdang", "Palata"
Incorporation of corn stalks during land preparation for the succeeding crop.
Location upland to hillyland and highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-1500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-3000
Landform footslopes- hillslopes; plateau/plains
Slope gentle-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50 - > 120 ; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-5
Land tenure titled, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline; and reduced organic matter content
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic Measures: RehabilitationTechnical function Increase soil fertility and organic matter
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Equiipment (animal traction) - 1,500 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seeds, fertilizer, biocides) - 7,700 P/ha; Others (planting, Harvesting, Maintenance) - 4,500 P/ha; Total cost - 13,700 P/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.56 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.04 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.98 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.16 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.74 Low
-
Planted Vegetative Strips (PVS)
Planting of economic crops/forages in strips along the contour to control soil loss through erosion.
Location lowland; upland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100; 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-2000
Landform hillslopes; plateaus/plains
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of top soil; surface erosion
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic Measures; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Control; dispersed runoff; imped and retard
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Planting of Alley crops; contouring; planting of vegetative strips. Establishment inputs and costs: Labor - 950 P/ha; Equipment (animal traction) - 600 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seeds and seedlings) - 5,300 P/ha. Total Cost - 6,850 P/ha.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.81 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.69 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.94 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.53 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.97 Medium
-
Windbreaks
Planting of herbaceous plants or trees along property boundaries to serve as windbreaks and as sources of fodder and fuel.
Location lowland; upland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) < 100; 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform footslopes; hillslopes
Slope rolling-hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level > 120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse agro-silvo pastoralism, rainfed
Land degradation soil erosion by wind, loss of top soil
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; PreventionTechnical function Reduction in wind speed
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment inputs and cost per ha (seeding /planting): Labor - 1,880 P/ha'; Tools - 250 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seedling, stem cuttings) - 800 P/ha. Total Cost - 2,930 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Removal of dead branches (trees); Cutting of grasses. Maintenance/recurrent cost per ha per year: Labor - 700 P/ha-year; Minor tools - 300 P/ha; Total recurrent cost - 1,000 P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.57 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.44 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.66 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.32 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.99 Low
-
Rainfed paddy rice terraces
"Palayan"
Terraces supporting rainfed paddy rice on steep mountain slopes: these have been in existence for more than a thousand years.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 1500-2500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-3000
Landform mountain slopes
Slope hilly - steep
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 80-120; > 120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha)
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of topsoil/surface erosion; chemical soil deterioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures (Bench Terraces); Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Control of dispersed runoff: retain trap; increase/maintain water stored in the soil; reduction of slope angle; reduction of slope length; indirect maintenance of fertility
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Levelling by moving soil from upslope to the downslope part; construction of bunds (lip at the terrace ridge) of about 50-100 cm; determination of contour lines. Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 115,000 P/ha; Equipment - 10,000 P/ha; Total cost - 125,000 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Weeding by cutting grasses on the bund/riser using hand tools, hoeing; Land preparation by puddling, in most cases the use of animal traction is not possible because of the steepness of the slope and height of the risers; Repairing breached portion of the bunds, adding few centimeters in the process. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha per year: Labor - 3,000 P/ha-year; Equipment (farm tools) - 1000 P/ha-year; Total maintenance cost - 4,000 P/ha-year. Remarks: The costs of establishment are just estimates as new terrace construction no longer takes place in the study area. The land has already been terraced for centuries. The maintenance costs assumes minor and light maintenance and does not include major repairs of bunds.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.91 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.67 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.93 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.69 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.20 Medium
-
Stone bunds and small basins
"Pamugong sa yuta (Cebuano)"
Piling of stones and rocks along the contour to control run-off and soil erosion. It is also about the creation of small basins by removing stones and using them as barriers.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1,500-2,000
Landform hill slopes
Slope rolling - hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level > 120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Surface soil erosion, top soil removal
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures; Mitigation and rehabilitationTechnical function control of concentrated runoff; retain/trap
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Contouring; gathering and piling of stones along contour with development of small basin for rainwater impoundment. Establishment inputs and cost per ha. Labor - 47,000 P/ha; Equipment - 1,000 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 1,800 P/ha.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.46 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.15 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.50 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.47 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.58 Low
-
Vetiver grass system or Vetiver grass technology
"Mora, Moras, Amora and Modas in the different regions in the Philippines"
Vetiver grass used as contour hedgerows in sloping agricultural land used for annual crops.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform hillslopes
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80 ; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping rainfed
Land degradation Surface erosion by water, loss of top soil
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; Mtigation and preventionTechnical function control dispersed runoff, retain top soil; reduction of slope length
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Planting vertiver grass along contour; Replacement/replanting gaps. Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 2,350 P/ha; Seedlings - 4,700 P/ha; Total Cost - 7,050 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Pruning. Maintenance and recurrent inputs and cost per ha per year: Labor - 1,000 P/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.38 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.14 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.77 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.51 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.80 Low
-
Littuko Growing for Forest Enhancement
Growing of rattan is done by upland farmers as part of the Community Based Forest Management (CBFM).
Location upland to hillyland and higland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500; 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform hillslopes
Slope hilly to steep
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50-1
Land tenure communal, organized
Landuse Natural;; Other: Grazing land; forest
Land degradation Biological degradation: reduction of vegetation cover; loss of habitat
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; RehabilitationTechnical function Promotion of vegetation species and varieties; conservation of trees that serve as hosts; increase organic matter; increase biomass
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Nursery establishment through seedbed; transplanting. Establishment per unit: Labor - 400 P/unit; Agricultural inputs (incl. seeds) - 10,400 P/ha; Total Cost -10,800/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.65 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.48 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.93 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.39 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.45 Medium
-
Rockwall Terracing
Rockwall terracing refers to the piling of stones or rocks along contour lines to reduce soil erosion in hilly areas.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform hillslopes-mountain slopes
Slope rolling - hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure not titled, individual
Landuse Annual cropping; mixed grazing land, rainfed and irrigated
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of topsoil/surface runoff
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Strucutural Measures; RehabilitationTechnical function control of dispersed runoff: retain trap; retain /trap; control concentrated runoff: retain trap; control soil erosion
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Contouring; Digging along contour; Gathering and piling of stones along contour. Establishment inpputs and costs per unit (ha): Labor - 37,800 P/ha; Equipment - 1,000 P/ha; Total cost - 38,800 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent of activities: Re-piling of stones and rocks that are dislodged. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per unit (ha) per year: Labor - 1,000 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.30 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.19 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.66 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.28 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.43 Low
-
Seed Production of Multipurpose Shrubs/Legumes
Seed production of multipurpose shrubs and legumes, a soil conservation practice in sloping areas wherein flemingia (Flemingia macrophylla) and Indigofera (Indigofera tinctoria) are densely planted along contours.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform hillslopes-mountainslopes
Slope rolling-hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50-1
Land tenure titled, individual
Landuse Trees and shrubs cropping: Forests/woodlands: natural cropland
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of topsoil/ surface runoff; chemical deterioraton-fertlity decline; biological degradation
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; RehabilitationTechnical function control of dispersed runoff-retain/trap; control of concentrated runoff; retain/trap; improvement of ground cover; promotion of vegetation species and varieties
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Land preparation; Plowing, harrowing and furrowing; Establishment of contour lines and laying out. Establishment inputs and costs per unit (ha): Labor - 2,300 P/ha; Equipment (bamboo pegs) - 150 P/ha; Seeds - 2,100 P/ha; Total Cost - 4,550 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Weeding/hilling-up; Harvesting; Sun drying; Manual threshing; Harvesting of Flemengia and Indigofera. Maintenance/recurrent costs: Labor - 2,100 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.06 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.47 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.95 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.41 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.89 Medium
-
Contour Farming Using Hedgerows
"Contour Farming"
Contour farming is a technology practiced in sloping areas in which hedgerows are established along the contours and other annual/cash crops are grown in the alleys between the hedges.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform hillslopes-mountain slopes
Slope rolling - hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) < 0.50
Land tenure not titled, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of topsoil/ surface erosion; chemical deterioration; fertillity decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Vegetative Measures; RehabilitationTechnical function Conrol of dispersed runoff: retain/trap; minimize soil erosion due to runoff; serve as soil nutrient traps
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Laying out and establishment of contour lines/hedges; Planting of hedgerows with Napier grass; Planting of perennial crops along contour. Establishment inputs and costs per unit (ha): Labor - 1,350 P/ha; Local materials (A-frame) - 100 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seedlings, herbecides) - 4,400 P/ha; Total cost - 5,850 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Land preparation of alley between hedges; furrowing; planting of corn (first cropping); Weeding; Harvesting of first crop; Planting of second crop (corn & peanut; Weeding; Harvesting of second crop. Maitenance/recurrent inputs and cost per ha per year: Labor - 1,950 P/ha-year; Equipment (animal traction)/ - 300 P/ha-year; Agricultural inputs (seeds and fertilizer) - 2,200 P/ha-year: Total maintenance cost - 4,450 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.03 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.76 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.08 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.90 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.77 High
-
Vegetable Terracing
Vegetable terracing is a technology practiced at which point terraces are established from the contours along mountain slope for crop production.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 2000-2500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform hillslopes-mountainslopes
Slope rolling-hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50;low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50-1
Land tenure titled, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, Forest/woodlandrest/woodlands
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of topsoil/surface erosion; chemical soil deterioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Structural Measures; Mitigation/ReductionTechnical function Control of dspersed runoff: impede/retart; control concentrated runoff: impede/retard; reduction of slope angle
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Establishment of terraces. Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 25,100 P/ha; Minor tools - 600 P/ha; Total cost - 25,700 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Land preparation; application of chicken manure; Planting; hilling up including application of fertilizer; Weeding; Spraying of insecticides; Harvesting. Maintenance/recurrent costs per ha per year: Labor - 14,570 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (fertilizer, compost/manure, insecticides) - 43,300 P/ha-year. Total maintenance/recurrent costs - 57,870 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.16 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.88 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.82 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.56 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.42 Medium
-
Alternate Wetting and Drying
Alternate Wetting and Drying is a water-use management technique wherein irrigation water input could be substantially reduced to as much as 35% without significantly affecting rice yields.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) < 100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform plain
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level > 120 ; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50-1
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual Cropping, irrigated
Land degradation Water degradation, change in quantity of surface water
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Management Measures- Major changes in timing of activities; PreventionTechnical function More efficient water use
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: 1) Preparation of PVC/bamboo tubes; 2) Perforating the sides of the tubes with many holes; Establishment inputs and cost per unit: Labor - 160 P/pc; Materials: PVC - 210 P/pc; Total Cost - 370P/pc
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.88 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.33 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.92 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.59 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.72 Medium
-
Trees as Buffer Zones
Trees as buffer zones are vegetative measures established in the area to prevent pest from crossing in between blocks. Further, the technology provides haven for flora and fauna which are endemic in the area.
Location upland to hillyland; highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500; 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform hillslopes; valley
Slope gentle - moderate
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; 80-120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Trees and shrubs
Land degradation Biological degradation; loss of habitats
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; Mitigation and preventionTechnical function Control of raindrop splash; control of dispersed runoff; stabilization of soil; reduction in wind speed; increase biomass; spatial arrangement and diversification of land use; improve biodiversity
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Grass Brushing; Hole Digging; Planting. Establishment inputs: Labor - 5,500 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent cost per hac per year: Labor - 3,700 P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.80 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.63 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.08 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.66 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.17 Medium
-
Pressing of Cogon Grass (Imperata cylindrica)
An indigenous technology of enhancing wildling growth by pressing of cogon grass.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform hillslopes; mountain slopes
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 50-100
Land tenure Lands owned by the state; Land user rights: open access (unorganized)
Landuse Natural; Deforested Land
Land degradation Biological degradation; loss of habitats
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures, Others (Suppressing of Cogon; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Enhance the growth of wildling by controlling the growth of fast-growing grasses (cogon); control/avoid forest fires
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Identification of wildlings (2 feet high); Ring weeding; Pressing of cogon away from wildlings; Application of fertilizers. Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 950 P/ha; Construction material (wood and rope) - 200 P/ha; Total Cost - P 1,150 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Pressing of Cogon (Labor) - 210 P/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 2.68 Negligible
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
2.52 Negligible
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.22 Low
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
2.67 Negligible
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 11.09 Low
-
Firebreaks/Greenbreaks
Gaps in vegetation or other combustible material that act as barriers to prevent and/ or control the spreading of forest fires to other areas.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform hillslopes; mountain slopes
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 50-100
Land tenure Lands owned by the state; Land user rights: open access (unorganized)
Landuse Plantation; afforestation, tree generation
Land degradation Biological degradation; detrimental effects of fire
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures, Others (Suppressing of Cogon; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Control fires; reduction of dry materials (fuel for wildfires)
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Clearing of Cogon in the firelines; Planting of kakawate cuttings. Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 1,250 P/ha. Maintenance: 500 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.11 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.16 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.86 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.36 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.49 Low
-
Ecological engineering for irrigated lowland rice ecosystem
Ecological engineering for lowland rice ecosystem by promoting and planting of flower strips in rice fields.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform plateau/plains
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 0-20; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5-1
Land tenure titled land, individual; water use rights- communal (organised)
Landuse Annual cropping, full irrigation
Land degradation Biological degradation: increase of pests/diseases, lost of predators
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; Others (Annual Flower Strips; Prevention and Mitigation/ReductionTechnical function Biological control reduces pollution by agro-chemicals
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Flowering plant seed collection; flowering plant nursery establishment; transplanting flowering plants. Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 4,730P/ha; Agricultural inputs (fertilizer, compost/manure - 1,600 P/ha; Total Cost - 6,330 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Flowering plant maintenance, i.e. trimming, removal of volunteer seedlings out of the strips and thinning during cropping season; Watering and replacement in times of long drought fallow period. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha per year: Labor - 1,880 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.08 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.87 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.05 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.64 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.64 High
-
Sediment Traps
"Catch basin, silt traps, cascading canals, trenches, ditches"
Sediment traps are structures built in the area which includes cascading catchment canal, silt traps and catch basin along perimeter, between pineapple fields and along diversion ditches to collect run-off during rains, preventing and minimizing the eroded soils cascading into natural bodies of water.
Location upland to hillyland; highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500; 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform hillslopes; valley floors
Slope gentle - moderate
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; 80-120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual; land user right - leased
Landuse Perennial; non-woody: Other: waterways, drainage lines, ponds, dams (after)
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of top soil; surface erosion
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures (Cascading canals and Silt Traps); Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Sediment retention/trapping, sediment harvesting; Control of dispersed runoff; retain/trap, impede/retard; control of concentrated runoff; retain/trap, impede/retard, drain/divert.
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activiteis: Excavation of canal; construction of bed; constructiobn of trenches. Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 2,530 P/ha; Equipment - 3,360 P/ha. Maintenance activities: Desilting. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha: Labor - P7,300 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.33 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.12 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.79 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.60 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.84 Low
-
Contour Straight Block Layout
It is a package of soil and water conservation technology that integrates contouring, bedding, and blocking.
Location upland to hillyland; highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500; 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform hillslopes; valley
Slope gentle - moderate
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; 80-120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual; land user right - leased
Landuse Perennial; non-woody (herbaceous)
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of top soil; surface erosion
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Vegetative Measures; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Control of raindrop splash; control of dispersed runoff; retain/trap, impede/retard; control of concentrated runoff; retain/trap, impede/retard, drain/divert
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Bedding, harrowing, Mulching, Planting materials (pineapple); plowing, construction of vegetative strips (laid out during the land preparation). Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 6,720 P/ha; Equipment (machine use) - 10, 580/ P/ha; Agricultural inputs: planting materials (pineapple) - 10, 200 P/ha; Total Cost - 27, 205 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent cost: Labor - 13,100 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.80 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.33 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.70 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.40 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.23 Medium
-
Modified Rapid Composting
Modified Rapid Composting is the in situ decomposition of rice straw using compost fungus activator, Trichoderma harzianum or Effective Microorganism, help in utilizing the residual Nitrogen-Phosphorus-Potassium (NPK) from the decomposed rice straw.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform plateau/plains
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level >120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure individual; titled
Landuse Annual cropping; full irrigation
Land degradation Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Organic matter / soil fertility; Mitigation /ReductionTechnical function increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling); - increase in organic matter
Establishment input and cost per ha Maintenance and recurrent activties: Labor for spreading rice straws - 1,300P/ha/year; Spraying of effective microorganism solution - 700 P/ha-year; Total - 2,000P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.04 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.81 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.02 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.49 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.36 Medium
-
Compact Farming for Vegetables Production
Landusers are organized into a group or association to undertake jointly activities in the farm which include operation, input procurement, and marketing of produced crops.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500 - 1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform footslopes to hillslopes
Slope moderate to rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; medium
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5-1 ; 1- 2
Land tenure communal, organised
Landuse Annual cropping Mixed: Agroforestry (before) Cropland: Annual cropping (after) mixed rainfed - irrigated
Land degradation Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, acidification
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Organic matter / soil fertility; Mitgation/reductionTechnical function Increase in organic matter; increase in nutrient availability
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Clearing of the area. Establisment cost: 10,400 P/ha. Maintenance and recurrent activities: Plowing, harrowing, establishment of Plots, Organic Fertilizer Application; transplanting, watering spraying of botanical pesticide, and harvesting. Maintenance and recurrent costs: Labor - 11, 400 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seedlings and fertilizers) - 7,850 P/ha. Total - 19,290 P/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.14 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.77 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.55 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.12 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.58 Medium
-
Sweet Potato Relay Cropping
"Lapat System"
A farmer’s indigenous practice of growing sweet potato as a relay crop to its main crop of either rice or corn.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform hillslopes; mountain slopes
Slope rolling -hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50 -1
Land tenure Individual; mixed land ownership
Landuse Annual cropping; rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Biological degradation: reduction of vegetation cover
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Soil surface treatment Agronomic: Vegetation/soil cover; Mitigation/ReductionTechnical function control of raindrop splash - improvement of ground cover
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Agricultural inputs (corn seeds, rice seeds, sweet potato cuttings) - 5,100 P/ha; Maintenance and recurrent costs: clearing, plowing, harrowing, furrowing and planting of corn, rice and sweet potato. and spraying - 18,400 P/ha-year; Agricultural (insecticides) - 500 P/ha-year. Total 18,900 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.02 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.43 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.51 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
2.95 Negligible
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.91 Low
-
Organic-Based System of Rice Intensification (SRI)
Intensifying the irrigated rice production while at the same time reducing farm inputs including seeds, fertilizer, and water.
Location lowland; upland and hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100 ; 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform plateau/plains
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level >120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1 -2
Land tenure individual; titled
Landuse Annual cropping
Land degradation Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Management: Major change in timing of activities Agronomic: Organic matter / soil fertility. Prevention & Mitigation/reductionTechnical function increase in organic matter; increase / maintain water stored in soil
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Planting of rice seeds, raising of ducks. Establishment cost of inputs: Ducks - 8,300 P/ha; rice seeds - 900 P/ha. Total - 9,200 P/ha. Maintenance and recurrent activities: fertilizer application (compost); harvesting; weeding; first plowing; spraying of natural concoctions; organic fertilizer application; clearing; transplanting; second plowing. Maintenance and recurrent inputs and costs: Labor - 10,026 P/ha-year; Equipment - 6,200 P/ha-year; Fertilizers - 3,100 P/ha-year. Total - 19,326 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.99 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.75 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.02 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.63 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.39 Medium
-
Composting using Indigenous Microorganism (IMO)
Composting is the natural process of decomposition of organic matter by microorganisms under controlled conditions.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 1000-5000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform mountain slopes
Slope steep
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 0-20; medium
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5-1
Land tenure individual; titled
Landuse Annual cropping Perennial (non-woody) cropping Grazing land: Extensive grazing land (before) Cropland: Annual cropping (after) full irrigation
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Organic matter / soil fertility; Mitgation/reductionTechnical function Increase in organic matter; increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…); improvement of topsoil structure (compaction); increase of infiltration
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Inputs: Procurement of sprayer, shredder, seedling pots and trays; establishment of composite chamber (shed) - 115,500 P/unit. Maintenance and recurrent activities -Hauling of grass and weeds available in the farm; Shredding of grass and weeds; Spraying the shredded grass and weeds with indigenous microorganisms (IMO); Leave for 14 days to decompose; Application of Compost. Labor - 2,600P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.96 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.71 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.25 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.51 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.43 Medium
-
Organic Mulching
Organic mulching is a practice of applying thin layer of organic materials on the soil surface that decompose over time for the purpose of conserving soil moisture, reducing soil erosion, improving soil fertility, and reducing weed growth.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 1000-5000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform mountain slopes
Slope steep
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 0-20; medium
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5-1
Land tenure individual; titled
Landuse Annual cropping Perennial (non-woody) Grazing land: Extensive grazing land (before) Cropland: Annual cropping (after) full irrig
Land degradation Water degradation: aridification
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Soil surface treatment; Organic matter/ soil fertility; Vegetation/soil cover; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function control of raindrop splash ; improvement of ground cover; - increase in organic matter; increase / maintain water stored in soil
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment inputs: Shredder (Machine) - 104,400 P/unit; Sprayer - 1,000 P/unit. Maintenance/recurrent activities (hauling of grasses and weeds available in the farm, shredding of grasses and weeds, spreading of shredded grasses and weeds to the soil surface,spraying of IMO to the shredded grasses): Labor - 2,800 P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.00 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.54 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.21 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.30 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.05 Medium
-
Sugar Mill Wastewater Re-use for Irrigation
Re-using of wastewater to support agricultural crop production, as well as, to help in environmental protection
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform plateau/plain
Slope flat to gently sloping
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level
Land holding/hh (ha) 500-1000
Land tenure company
Landuse Annual Cropping; cropland
Land degradation Water degradation: decline of surface water quality
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural measures: sanitation/wastewater structures; management measures-waste managementTechnical function Conserve ecosystem; protect wateshed/downstream areas
Establishment input and cost per ha Not available
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.00 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.00 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.50 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
4.00 High
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.50 Medium
-
Highly Diversified Cropping in Live Trellis System
"Kakawate as live trellis "balag""
Gliricidia sepium locally known as "kakawate" served as live trellis / or anchorage for annual crops (mostly creeping-type vegetables) and erosion control measure. The technology is well-adopted in the community providing immediate food for the farmers and increased income due to diversified farming.
Location upland to hillyland; highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000 -2000
Landform footslopes and mountainslopes
Slope hilly to rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 51-80; moderately deep; medium to high fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5 - 1.0
Land tenure individual
Landuse Annual cropping: cropland; Mixed (crops/grazing) incl agroforestry
Land degradation Soil erosio by water: loss of topsoil/surface erosion; offsite degradation effects
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic measures - Vegetation/ soil cover, Organic matter/ soil fertility, : Soil surface treatment. Vegetative measures - V1: Tree and shrub coverTechnical function Improve production; prevent and reduce land degradation; preserve and improve biodiversity
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Manual labor for weeding, planting, fertilizer applicatio, harvesting and hauling - P3,600/ha; Planting materials - P2,550/ha; Fertilizers and biocides - P10,030/ha; Construction materials - P3,880; Total cost - P20, 060. Maintenance activities: Labor for weeding, trimming of kakawate, application of ferilizers, spraying - P4,500/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.20 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.50 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.00 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.50 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.20 Medium
-
Mangroves as Buffer against Natural Hazards
"Bakauan"
Mangroves "bakauan" are planted in the island coast to form barriers and as first line of defense during storm surges.
Location coastal area
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 0.00- 100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1,500 - 2,000
Landform Coast
Slope 0-2
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level Low
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5 - 1.0
Land tenure State
Landuse Forest/woodlands; crustaceans breeding ground
Land degradation Reduction of vegetation cover; loss of habitats
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetatative measures; prevent land degradationTechnical function Conserve ecosystem; preserve improve biodiversity; reduce disaster; adapt to CC; mitigate CC
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Labor - P2500/ha; Planting materials - P5000/ha; Total Cost -P7500. Maintenance and Recurrent Activities: Labor - P750/ha; Replanting materials - P250/ha; Total - P1,000/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.60 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.50 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.50 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
4.00 High
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.60 Medium
- All
- Soil Erosion by Water
- Soil Erosion by Wind
- Chemical Soil Deterioration
- Physical Soil Deterioration
- Water Degradation
- Biological Degradatiion
-
Conservation Tillage Practices for Corn Production
"Tipid Saka"
A crop production system which focuses on soil conservation and reducing excessive tillage operations, reduces labor and farm inputs while increasing productivity and profitability.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform plains
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure untitledland (leased)
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Chemical Soil Deterioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic measures: Prevention and mitigation/reductionTechnical function increased soil fertility and good soil structure for better nutrient and water uptake by plants
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment input and cost per ha: Labor - 6,950 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seeds, fertilizer, biocides, Bio-N) - 4,400 P/ha; Others (post harvest, market transport and packaging) - 10,810 P/ha. Total Cost - 22,160 P/ha.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.83 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.67 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.84 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.52 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.86 Medium
-
Natural Vegetative Strips (NVS)
Within individual cropland plots, strips of land are marked out on the contour and left unploughed in order to form permanent, cross-slope barriers of naturally established grasses and herbs.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500 -1500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-3000
Landform footslopes; hillslopes
Slope rolling-hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-80; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-20
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, trees and shrubs: rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of top soil; surface erosion; gully erosion; chemical soil deterioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter.
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Vegetative Measures; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Reduction of slope angle; reduction of slope length; control of dispersed runoff; increase infiltration and increase soil fertility
Establishment input and cost per ha Establisment activities: Lay out of contour using A-frame; placing wooden pegs along contours; seeding; transplanting; land preparation. Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 1000 P/ha; Equiipment (animal traction, tools, and stakes) - 3,300 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seeds, seedlings, fertilizer, biocides) - 9,000 P/ha; Total Cost - 13,300 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Plowing along the contour leaving unplowed strips; planting; mulching; fertilization, interim cultivation/weeding; plowing mulch into the soil; weeding slashing grass; spreading the cut materials evenly in the alleys; pruning. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and cost per ha per year: Labor -1,700 P/ha-year; Equipment (animal traction, tools) - 1,980 P/ha-year; Agricultural inputs (seeds, fertilizer, biocides) - 7,500 P/ha-year; Total maintenance cost - 11,180 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.81 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.56 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.95 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.63 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.95 Medium
-
In 'situ' Decomposition of Banana Stalk
"Palata System"
Leaving the trunk of a newly harvested banana standing beside a follower plant to provide nutrients and moisture especially during period of drought.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) < 100
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform plateau/plains
Slope flat-gently sloping
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level >120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 2-5; 500-1,000
Land tenure company leased
Landuse Perennial (non-woody) cropping, full irrigation
Land degradation Chemical soil detrioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, water degradation; aridification
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic Measures: Mitigation/reduction and rehabilitationTechnical function Increase soil fertility; Increase/maintain water stored in the soil
Establishment input and cost per ha Maintenance/recurrent activities: 1) Cutting of crown of newly harvested plants; Inputs: Labor - 2,350 P/ha-year; Equipment - cutting tools - 500 P/ha-year; Total Cost - 2,850P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.63 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.02 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.65 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
2.99 Negligible
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.29 Low
-
Small Water Impounding Project (SWIP)
Development of micro-catchment for soil and water conservation and for the provision of supplementary irrigation during the dry season.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-3000
Landform hillslopes; valley
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 80-120 ; >120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping; perennial crop
Land degradation Water degradation, aridification
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures; Mitigation/reduction and rehabilitationTechnical function Water harvesting nd increase water supply
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Clearing, staking and laying out; Stripping and excavation; embankment filling; pipe lay out and installation; riprapping; concrete works, embankment sodding; and canal excavation and lining. Establishment inputs and cost per ha of service area: Labor - 105,000 P/ha; Materials - 99,000 P/ha; 96,000 P/ha; Total Cost - 300,000 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent costs (Embankment maintenance, appurtenant structures maintenance, canal maintenance): Labor - 12,000 P/ha-year; Minor equipment - 3,000 P/ha-year; Total maintenance cost - 15,000 P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.26 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.62 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.05 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
4.04 High
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.97 High
-
Small Farm Reservoir (SFR)
"Tabon"
The Small Farm Rerservoir is an earth dam structure used to trap harvest and store rainfall and water runoff.
Location lowland; upland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) < 100; 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform plains/hillslopes
Slope rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; low organic matter content
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping
Land degradation soil erosion and excessive runoff; limited water supply
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures: Prevention and rhabilitationTechnical function Water harvesting/ increase water supply; Control dispersed runoff, retain/trapped; contol concentrated runoff: retain/trap.
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: 1) Laying-out & staking; 2) Clearing; 3) Excavation; 4) Spreading of fill materials; 5) Embankment filling and compaction; 6) pipe laying out and setting; and 7) canal/spillway construction. Total construction cost - 40,000 - 100,000 P/unit.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.03 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.40 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.96 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.97 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.36 Medium
-
Multi-Storey Cropping
"Maramihang Pagtatanim or Planting in Great Numbers"
Cultivating a mixture of crops with different heights (multi-storey) and growth characteristics which together optimise the use of soil, moisture and space.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform footslopes, ridges, and plateau/plain
Slope gentle - moderate
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 80-120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Agroforestry, rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of top soil/surface runoff; chemical soil deterioration; fertilit decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Vegetative Measures; PreventionTechnical function Control raindrop splash; improvement of ground cover
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment actvities: Planting of tallest storey (coconut); Planting of lowest storey (pineapple); Planting of lowest storey continued (root crops); Planting of middle storey (coffe and banana). Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 7,000 P/ha; Equipment (animal traction and farm tools) - 4, 230 P/ha; Agricultural (seedlings, fertilizer, biocides, compost/manure) - 54,000 P/ha; Total Cost - 65,230 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha per year: Labor - 14,100 P/ha-year; Agricultural (fertilizer, biocides) - 9,000 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.40 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.97 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.21 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.98 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 16.56 High
-
Residue Incorporation (Corn)
"Palugdang", "Palata"
Incorporation of corn stalks during land preparation for the succeeding crop.
Location upland to hillyland and highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-1500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-3000
Landform footslopes- hillslopes; plateau/plains
Slope gentle-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50 - > 120 ; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-5
Land tenure titled, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline; and reduced organic matter content
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic Measures: RehabilitationTechnical function Increase soil fertility and organic matter
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Equiipment (animal traction) - 1,500 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seeds, fertilizer, biocides) - 7,700 P/ha; Others (planting, Harvesting, Maintenance) - 4,500 P/ha; Total cost - 13,700 P/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.56 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.04 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.98 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.16 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.74 Low
-
Planted Vegetative Strips (PVS)
Planting of economic crops/forages in strips along the contour to control soil loss through erosion.
Location lowland; upland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100; 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-2000
Landform hillslopes; plateaus/plains
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of top soil; surface erosion
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic Measures; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Control; dispersed runoff; imped and retard
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Planting of Alley crops; contouring; planting of vegetative strips. Establishment inputs and costs: Labor - 950 P/ha; Equipment (animal traction) - 600 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seeds and seedlings) - 5,300 P/ha. Total Cost - 6,850 P/ha.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.81 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.69 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.94 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.53 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.97 Medium
-
Windbreaks
Planting of herbaceous plants or trees along property boundaries to serve as windbreaks and as sources of fodder and fuel.
Location lowland; upland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) < 100; 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform footslopes; hillslopes
Slope rolling-hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level > 120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse agro-silvo pastoralism, rainfed
Land degradation soil erosion by wind, loss of top soil
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; PreventionTechnical function Reduction in wind speed
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment inputs and cost per ha (seeding /planting): Labor - 1,880 P/ha'; Tools - 250 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seedling, stem cuttings) - 800 P/ha. Total Cost - 2,930 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Removal of dead branches (trees); Cutting of grasses. Maintenance/recurrent cost per ha per year: Labor - 700 P/ha-year; Minor tools - 300 P/ha; Total recurrent cost - 1,000 P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.57 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.44 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.66 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.32 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.99 Low
-
Rainfed paddy rice terraces
"Palayan"
Terraces supporting rainfed paddy rice on steep mountain slopes: these have been in existence for more than a thousand years.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 1500-2500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-3000
Landform mountain slopes
Slope hilly - steep
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 80-120; > 120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha)
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of topsoil/surface erosion; chemical soil deterioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures (Bench Terraces); Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Control of dispersed runoff: retain trap; increase/maintain water stored in the soil; reduction of slope angle; reduction of slope length; indirect maintenance of fertility
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Levelling by moving soil from upslope to the downslope part; construction of bunds (lip at the terrace ridge) of about 50-100 cm; determination of contour lines. Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 115,000 P/ha; Equipment - 10,000 P/ha; Total cost - 125,000 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Weeding by cutting grasses on the bund/riser using hand tools, hoeing; Land preparation by puddling, in most cases the use of animal traction is not possible because of the steepness of the slope and height of the risers; Repairing breached portion of the bunds, adding few centimeters in the process. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha per year: Labor - 3,000 P/ha-year; Equipment (farm tools) - 1000 P/ha-year; Total maintenance cost - 4,000 P/ha-year. Remarks: The costs of establishment are just estimates as new terrace construction no longer takes place in the study area. The land has already been terraced for centuries. The maintenance costs assumes minor and light maintenance and does not include major repairs of bunds.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.91 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.67 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.93 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.69 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.20 Medium
-
Stone bunds and small basins
"Pamugong sa yuta (Cebuano)"
Piling of stones and rocks along the contour to control run-off and soil erosion. It is also about the creation of small basins by removing stones and using them as barriers.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1,500-2,000
Landform hill slopes
Slope rolling - hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level > 120; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Surface soil erosion, top soil removal
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures; Mitigation and rehabilitationTechnical function control of concentrated runoff; retain/trap
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Contouring; gathering and piling of stones along contour with development of small basin for rainwater impoundment. Establishment inputs and cost per ha. Labor - 47,000 P/ha; Equipment - 1,000 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 1,800 P/ha.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.46 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.15 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.50 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.47 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.58 Low
-
Vetiver grass system or Vetiver grass technology
"Mora, Moras, Amora and Modas in the different regions in the Philippines"
Vetiver grass used as contour hedgerows in sloping agricultural land used for annual crops.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform hillslopes
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80 ; low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual cropping rainfed
Land degradation Surface erosion by water, loss of top soil
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; Mtigation and preventionTechnical function control dispersed runoff, retain top soil; reduction of slope length
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Planting vertiver grass along contour; Replacement/replanting gaps. Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 2,350 P/ha; Seedlings - 4,700 P/ha; Total Cost - 7,050 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Pruning. Maintenance and recurrent inputs and cost per ha per year: Labor - 1,000 P/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.38 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.14 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.77 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.51 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.80 Low
-
Littuko Growing for Forest Enhancement
Growing of rattan is done by upland farmers as part of the Community Based Forest Management (CBFM).
Location upland to hillyland and higland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500; 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform hillslopes
Slope hilly to steep
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50-1
Land tenure communal, organized
Landuse Natural;; Other: Grazing land; forest
Land degradation Biological degradation: reduction of vegetation cover; loss of habitat
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; RehabilitationTechnical function Promotion of vegetation species and varieties; conservation of trees that serve as hosts; increase organic matter; increase biomass
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Nursery establishment through seedbed; transplanting. Establishment per unit: Labor - 400 P/unit; Agricultural inputs (incl. seeds) - 10,400 P/ha; Total Cost -10,800/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.65 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.48 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.93 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.39 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.45 Medium
-
Rockwall Terracing
Rockwall terracing refers to the piling of stones or rocks along contour lines to reduce soil erosion in hilly areas.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform hillslopes-mountain slopes
Slope rolling - hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure not titled, individual
Landuse Annual cropping; mixed grazing land, rainfed and irrigated
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of topsoil/surface runoff
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Strucutural Measures; RehabilitationTechnical function control of dispersed runoff: retain trap; retain /trap; control concentrated runoff: retain trap; control soil erosion
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Contouring; Digging along contour; Gathering and piling of stones along contour. Establishment inpputs and costs per unit (ha): Labor - 37,800 P/ha; Equipment - 1,000 P/ha; Total cost - 38,800 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent of activities: Re-piling of stones and rocks that are dislodged. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per unit (ha) per year: Labor - 1,000 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.30 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.19 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.66 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.28 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.43 Low
-
Seed Production of Multipurpose Shrubs/Legumes
Seed production of multipurpose shrubs and legumes, a soil conservation practice in sloping areas wherein flemingia (Flemingia macrophylla) and Indigofera (Indigofera tinctoria) are densely planted along contours.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform hillslopes-mountainslopes
Slope rolling-hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50-1
Land tenure titled, individual
Landuse Trees and shrubs cropping: Forests/woodlands: natural cropland
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of topsoil/ surface runoff; chemical deterioraton-fertlity decline; biological degradation
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; RehabilitationTechnical function control of dispersed runoff-retain/trap; control of concentrated runoff; retain/trap; improvement of ground cover; promotion of vegetation species and varieties
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Land preparation; Plowing, harrowing and furrowing; Establishment of contour lines and laying out. Establishment inputs and costs per unit (ha): Labor - 2,300 P/ha; Equipment (bamboo pegs) - 150 P/ha; Seeds - 2,100 P/ha; Total Cost - 4,550 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Weeding/hilling-up; Harvesting; Sun drying; Manual threshing; Harvesting of Flemengia and Indigofera. Maintenance/recurrent costs: Labor - 2,100 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.06 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.47 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.95 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.41 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.89 Medium
-
Contour Farming Using Hedgerows
"Contour Farming"
Contour farming is a technology practiced in sloping areas in which hedgerows are established along the contours and other annual/cash crops are grown in the alleys between the hedges.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform hillslopes-mountain slopes
Slope rolling - hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) < 0.50
Land tenure not titled, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of topsoil/ surface erosion; chemical deterioration; fertillity decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Vegetative Measures; RehabilitationTechnical function Conrol of dispersed runoff: retain/trap; minimize soil erosion due to runoff; serve as soil nutrient traps
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Laying out and establishment of contour lines/hedges; Planting of hedgerows with Napier grass; Planting of perennial crops along contour. Establishment inputs and costs per unit (ha): Labor - 1,350 P/ha; Local materials (A-frame) - 100 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seedlings, herbecides) - 4,400 P/ha; Total cost - 5,850 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Land preparation of alley between hedges; furrowing; planting of corn (first cropping); Weeding; Harvesting of first crop; Planting of second crop (corn & peanut; Weeding; Harvesting of second crop. Maitenance/recurrent inputs and cost per ha per year: Labor - 1,950 P/ha-year; Equipment (animal traction)/ - 300 P/ha-year; Agricultural inputs (seeds and fertilizer) - 2,200 P/ha-year: Total maintenance cost - 4,450 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.03 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.76 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.08 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.90 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.77 High
-
Vegetable Terracing
Vegetable terracing is a technology practiced at which point terraces are established from the contours along mountain slope for crop production.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 2000-2500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform hillslopes-mountainslopes
Slope rolling-hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50;low fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50-1
Land tenure titled, individual
Landuse Annual cropping, Forest/woodlandrest/woodlands
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of topsoil/surface erosion; chemical soil deterioration; fertility decline and reduced organic matter
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Structural Measures; Mitigation/ReductionTechnical function Control of dspersed runoff: impede/retart; control concentrated runoff: impede/retard; reduction of slope angle
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Establishment of terraces. Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 25,100 P/ha; Minor tools - 600 P/ha; Total cost - 25,700 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Land preparation; application of chicken manure; Planting; hilling up including application of fertilizer; Weeding; Spraying of insecticides; Harvesting. Maintenance/recurrent costs per ha per year: Labor - 14,570 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (fertilizer, compost/manure, insecticides) - 43,300 P/ha-year. Total maintenance/recurrent costs - 57,870 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.16 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.88 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.82 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.56 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.42 Medium
-
Alternate Wetting and Drying
Alternate Wetting and Drying is a water-use management technique wherein irrigation water input could be substantially reduced to as much as 35% without significantly affecting rice yields.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) < 100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform plain
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level > 120 ; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50-1
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Annual Cropping, irrigated
Land degradation Water degradation, change in quantity of surface water
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Management Measures- Major changes in timing of activities; PreventionTechnical function More efficient water use
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: 1) Preparation of PVC/bamboo tubes; 2) Perforating the sides of the tubes with many holes; Establishment inputs and cost per unit: Labor - 160 P/pc; Materials: PVC - 210 P/pc; Total Cost - 370P/pc
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.88 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.33 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.92 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.59 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.72 Medium
-
Trees as Buffer Zones
Trees as buffer zones are vegetative measures established in the area to prevent pest from crossing in between blocks. Further, the technology provides haven for flora and fauna which are endemic in the area.
Location upland to hillyland; highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500; 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform hillslopes; valley
Slope gentle - moderate
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; 80-120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual
Landuse Trees and shrubs
Land degradation Biological degradation; loss of habitats
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; Mitigation and preventionTechnical function Control of raindrop splash; control of dispersed runoff; stabilization of soil; reduction in wind speed; increase biomass; spatial arrangement and diversification of land use; improve biodiversity
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Grass Brushing; Hole Digging; Planting. Establishment inputs: Labor - 5,500 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent cost per hac per year: Labor - 3,700 P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.80 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.63 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.08 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.66 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.17 Medium
-
Pressing of Cogon Grass (Imperata cylindrica)
An indigenous technology of enhancing wildling growth by pressing of cogon grass.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform hillslopes; mountain slopes
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 50-100
Land tenure Lands owned by the state; Land user rights: open access (unorganized)
Landuse Natural; Deforested Land
Land degradation Biological degradation; loss of habitats
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures, Others (Suppressing of Cogon; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Enhance the growth of wildling by controlling the growth of fast-growing grasses (cogon); control/avoid forest fires
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Identification of wildlings (2 feet high); Ring weeding; Pressing of cogon away from wildlings; Application of fertilizers. Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 950 P/ha; Construction material (wood and rope) - 200 P/ha; Total Cost - P 1,150 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Pressing of Cogon (Labor) - 210 P/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 2.68 Negligible
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
2.52 Negligible
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.22 Low
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
2.67 Negligible
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 11.09 Low
-
Firebreaks/Greenbreaks
Gaps in vegetation or other combustible material that act as barriers to prevent and/ or control the spreading of forest fires to other areas.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform hillslopes; mountain slopes
Slope moderate-rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 50-100
Land tenure Lands owned by the state; Land user rights: open access (unorganized)
Landuse Plantation; afforestation, tree generation
Land degradation Biological degradation; detrimental effects of fire
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures, Others (Suppressing of Cogon; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Control fires; reduction of dry materials (fuel for wildfires)
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Clearing of Cogon in the firelines; Planting of kakawate cuttings. Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 1,250 P/ha. Maintenance: 500 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.11 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.16 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.86 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.36 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.49 Low
-
Ecological engineering for irrigated lowland rice ecosystem
Ecological engineering for lowland rice ecosystem by promoting and planting of flower strips in rice fields.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform plateau/plains
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 0-20; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5-1
Land tenure titled land, individual; water use rights- communal (organised)
Landuse Annual cropping, full irrigation
Land degradation Biological degradation: increase of pests/diseases, lost of predators
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetative Measures; Others (Annual Flower Strips; Prevention and Mitigation/ReductionTechnical function Biological control reduces pollution by agro-chemicals
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Flowering plant seed collection; flowering plant nursery establishment; transplanting flowering plants. Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 4,730P/ha; Agricultural inputs (fertilizer, compost/manure - 1,600 P/ha; Total Cost - 6,330 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent activities: Flowering plant maintenance, i.e. trimming, removal of volunteer seedlings out of the strips and thinning during cropping season; Watering and replacement in times of long drought fallow period. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha per year: Labor - 1,880 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.08 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.87 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.05 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.64 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.64 High
-
Sediment Traps
"Catch basin, silt traps, cascading canals, trenches, ditches"
Sediment traps are structures built in the area which includes cascading catchment canal, silt traps and catch basin along perimeter, between pineapple fields and along diversion ditches to collect run-off during rains, preventing and minimizing the eroded soils cascading into natural bodies of water.
Location upland to hillyland; highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500; 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform hillslopes; valley floors
Slope gentle - moderate
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; 80-120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual; land user right - leased
Landuse Perennial; non-woody: Other: waterways, drainage lines, ponds, dams (after)
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of top soil; surface erosion
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural Measures (Cascading canals and Silt Traps); Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Sediment retention/trapping, sediment harvesting; Control of dispersed runoff; retain/trap, impede/retard; control of concentrated runoff; retain/trap, impede/retard, drain/divert.
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activiteis: Excavation of canal; construction of bed; constructiobn of trenches. Establishment inputs and costs per ha: Labor - 2,530 P/ha; Equipment - 3,360 P/ha. Maintenance activities: Desilting. Maintenance/recurrent inputs and costs per ha: Labor - P7,300 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.33 Low
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.12 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.79 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.60 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.84 Low
-
Contour Straight Block Layout
It is a package of soil and water conservation technology that integrates contouring, bedding, and blocking.
Location upland to hillyland; highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500; 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform hillslopes; valley
Slope gentle - moderate
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; 80-120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure titled land, individual; land user right - leased
Landuse Perennial; non-woody (herbaceous)
Land degradation Soil erosion by water; loss of top soil; surface erosion
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic and Vegetative Measures; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function Control of raindrop splash; control of dispersed runoff; retain/trap, impede/retard; control of concentrated runoff; retain/trap, impede/retard, drain/divert
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Bedding, harrowing, Mulching, Planting materials (pineapple); plowing, construction of vegetative strips (laid out during the land preparation). Establishment inputs and cost per ha: Labor - 6,720 P/ha; Equipment (machine use) - 10, 580/ P/ha; Agricultural inputs: planting materials (pineapple) - 10, 200 P/ha; Total Cost - 27, 205 P/ha. Maintenance/recurrent cost: Labor - 13,100 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.80 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.33 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.70 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.40 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.23 Medium
-
Modified Rapid Composting
Modified Rapid Composting is the in situ decomposition of rice straw using compost fungus activator, Trichoderma harzianum or Effective Microorganism, help in utilizing the residual Nitrogen-Phosphorus-Potassium (NPK) from the decomposed rice straw.
Location lowland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1500-2000
Landform plateau/plains
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level >120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1-2
Land tenure individual; titled
Landuse Annual cropping; full irrigation
Land degradation Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Organic matter / soil fertility; Mitigation /ReductionTechnical function increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling); - increase in organic matter
Establishment input and cost per ha Maintenance and recurrent activties: Labor for spreading rice straws - 1,300P/ha/year; Spraying of effective microorganism solution - 700 P/ha-year; Total - 2,000P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.04 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.81 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.02 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.49 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.36 Medium
-
Compact Farming for Vegetables Production
Landusers are organized into a group or association to undertake jointly activities in the farm which include operation, input procurement, and marketing of produced crops.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500 - 1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform footslopes to hillslopes
Slope moderate to rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 50-80; medium
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5-1 ; 1- 2
Land tenure communal, organised
Landuse Annual cropping Mixed: Agroforestry (before) Cropland: Annual cropping (after) mixed rainfed - irrigated
Land degradation Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, acidification
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Organic matter / soil fertility; Mitgation/reductionTechnical function Increase in organic matter; increase in nutrient availability
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Clearing of the area. Establisment cost: 10,400 P/ha. Maintenance and recurrent activities: Plowing, harrowing, establishment of Plots, Organic Fertilizer Application; transplanting, watering spraying of botanical pesticide, and harvesting. Maintenance and recurrent costs: Labor - 11, 400 P/ha; Agricultural inputs (seedlings and fertilizers) - 7,850 P/ha. Total - 19,290 P/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.14 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.77 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.55 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.12 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.58 Medium
-
Sweet Potato Relay Cropping
"Lapat System"
A farmer’s indigenous practice of growing sweet potato as a relay crop to its main crop of either rice or corn.
Location upland to hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform hillslopes; mountain slopes
Slope rolling -hilly
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 20-50; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.50 -1
Land tenure Individual; mixed land ownership
Landuse Annual cropping; rainfed
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Biological degradation: reduction of vegetation cover
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Soil surface treatment Agronomic: Vegetation/soil cover; Mitigation/ReductionTechnical function control of raindrop splash - improvement of ground cover
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Agricultural inputs (corn seeds, rice seeds, sweet potato cuttings) - 5,100 P/ha; Maintenance and recurrent costs: clearing, plowing, harrowing, furrowing and planting of corn, rice and sweet potato. and spraying - 18,400 P/ha-year; Agricultural (insecticides) - 500 P/ha-year. Total 18,900 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.02 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.43 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.51 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
2.95 Negligible
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 13.91 Low
-
Organic-Based System of Rice Intensification (SRI)
Intensifying the irrigated rice production while at the same time reducing farm inputs including seeds, fertilizer, and water.
Location lowland; upland and hillyland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) <100 ; 100-500
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000-1500
Landform plateau/plains
Slope flat
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level >120; medium fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 1 -2
Land tenure individual; titled
Landuse Annual cropping
Land degradation Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Management: Major change in timing of activities Agronomic: Organic matter / soil fertility. Prevention & Mitigation/reductionTechnical function increase in organic matter; increase / maintain water stored in soil
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Planting of rice seeds, raising of ducks. Establishment cost of inputs: Ducks - 8,300 P/ha; rice seeds - 900 P/ha. Total - 9,200 P/ha. Maintenance and recurrent activities: fertilizer application (compost); harvesting; weeding; first plowing; spraying of natural concoctions; organic fertilizer application; clearing; transplanting; second plowing. Maintenance and recurrent inputs and costs: Labor - 10,026 P/ha-year; Equipment - 6,200 P/ha-year; Fertilizers - 3,100 P/ha-year. Total - 19,326 P/ha-year.
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.99 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.75 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.02 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.63 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.39 Medium
-
Composting using Indigenous Microorganism (IMO)
Composting is the natural process of decomposition of organic matter by microorganisms under controlled conditions.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 1000-5000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform mountain slopes
Slope steep
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 0-20; medium
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5-1
Land tenure individual; titled
Landuse Annual cropping Perennial (non-woody) cropping Grazing land: Extensive grazing land (before) Cropland: Annual cropping (after) full irrigation
Land degradation Soil erosion by water: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Chemical soil deterioration: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Organic matter / soil fertility; Mitgation/reductionTechnical function Increase in organic matter; increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…); improvement of topsoil structure (compaction); increase of infiltration
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Inputs: Procurement of sprayer, shredder, seedling pots and trays; establishment of composite chamber (shed) - 115,500 P/unit. Maintenance and recurrent activities -Hauling of grass and weeds available in the farm; Shredding of grass and weeds; Spraying the shredded grass and weeds with indigenous microorganisms (IMO); Leave for 14 days to decompose; Application of Compost. Labor - 2,600P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.96 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.71 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.25 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.51 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.43 Medium
-
Organic Mulching
Organic mulching is a practice of applying thin layer of organic materials on the soil surface that decompose over time for the purpose of conserving soil moisture, reducing soil erosion, improving soil fertility, and reducing weed growth.
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 1000-5000
Annual rainfall (mm) 3000-4000
Landform mountain slopes
Slope steep
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 0-20; medium
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5-1
Land tenure individual; titled
Landuse Annual cropping Perennial (non-woody) Grazing land: Extensive grazing land (before) Cropland: Annual cropping (after) full irrig
Land degradation Water degradation: aridification
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic: Soil surface treatment; Organic matter/ soil fertility; Vegetation/soil cover; Prevention and mitigationTechnical function control of raindrop splash ; improvement of ground cover; - increase in organic matter; increase / maintain water stored in soil
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment inputs: Shredder (Machine) - 104,400 P/unit; Sprayer - 1,000 P/unit. Maintenance/recurrent activities (hauling of grasses and weeds available in the farm, shredding of grasses and weeds, spreading of shredded grasses and weeds to the soil surface,spraying of IMO to the shredded grasses): Labor - 2,800 P/ha-year
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.00 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.54 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.21 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.30 Low
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.05 Medium
-
Sugar Mill Wastewater Re-use for Irrigation
Re-using of wastewater to support agricultural crop production, as well as, to help in environmental protection
Location highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 500-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 2000-3000
Landform plateau/plain
Slope flat to gently sloping
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level
Land holding/hh (ha) 500-1000
Land tenure company
Landuse Annual Cropping; cropland
Land degradation Water degradation: decline of surface water quality
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Structural measures: sanitation/wastewater structures; management measures-waste managementTechnical function Conserve ecosystem; protect wateshed/downstream areas
Establishment input and cost per ha Not available
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.00 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.00 Low
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.50 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
4.00 High
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.50 Medium
-
Highly Diversified Cropping in Live Trellis System
"Kakawate as live trellis "balag""
Gliricidia sepium locally known as "kakawate" served as live trellis / or anchorage for annual crops (mostly creeping-type vegetables) and erosion control measure. The technology is well-adopted in the community providing immediate food for the farmers and increased income due to diversified farming.
Location upland to hillyland; highland
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 100-1000
Annual rainfall (mm) 1000 -2000
Landform footslopes and mountainslopes
Slope hilly to rolling
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level 51-80; moderately deep; medium to high fertility
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5 - 1.0
Land tenure individual
Landuse Annual cropping: cropland; Mixed (crops/grazing) incl agroforestry
Land degradation Soil erosio by water: loss of topsoil/surface erosion; offsite degradation effects
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Agronomic measures - Vegetation/ soil cover, Organic matter/ soil fertility, : Soil surface treatment. Vegetative measures - V1: Tree and shrub coverTechnical function Improve production; prevent and reduce land degradation; preserve and improve biodiversity
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment activities: Manual labor for weeding, planting, fertilizer applicatio, harvesting and hauling - P3,600/ha; Planting materials - P2,550/ha; Fertilizers and biocides - P10,030/ha; Construction materials - P3,880; Total cost - P20, 060. Maintenance activities: Labor for weeding, trimming of kakawate, application of ferilizers, spraying - P4,500/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 4.20 High
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.50 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
4.00 High
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
3.50 Medium
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 15.20 Medium
-
Mangroves as Buffer against Natural Hazards
"Bakauan"
Mangroves "bakauan" are planted in the island coast to form barriers and as first line of defense during storm surges.
Location coastal area
Altitude, meters above sea level (masl) 0.00- 100
Annual rainfall (mm) 1,500 - 2,000
Landform Coast
Slope 0-2
Soil depth (cm) & fertility level Low
Land holding/hh (ha) 0.5 - 1.0
Land tenure State
Landuse Forest/woodlands; crustaceans breeding ground
Land degradation Reduction of vegetation cover; loss of habitats
Conservation measure & stages of intervention Vegetatative measures; prevent land degradationTechnical function Conserve ecosystem; preserve improve biodiversity; reduce disaster; adapt to CC; mitigate CC
Establishment input and cost per ha Establishment Activities: Labor - P2500/ha; Planting materials - P5000/ha; Total Cost -P7500. Maintenance and Recurrent Activities: Labor - P750/ha; Replanting materials - P250/ha; Total - P1,000/ha
Assessment of the technologyProduction and socio economic benefits
(2.68-4.40) 3.60 Medium
Socio-cultural benefits
(2.52 - 3.97)
3.50 Medium
Ecological benefits
(3.22 - 4.25)
3.50 Medium
Offsite benefits
(2.67 - 4.04)
4.00 High
Total benefits
(11.09 - 16.66) 14.60 Medium